The Week in Research Review, etc 11-5-18
The Week in Research Review, etc 11-5-18 was filled with more informative and eye-opening posts! Lots of visually stimulating posts to help clarify what exactly is going on in the hip joint with PROM. Another post that shows the suction effect from an intact hip labrum… amongst other great posts. Just some great stuff..hope you enjoy!
- Manual Forearm Resistance Drills
- ACL Graft Healing Times to Maturation
- Hip Capsule Stress with PROM External Rotation
- Muscle Activation Affected by Hip Thrust Variation
- Hip Thrust Form by Bret Contreras
- Hip Joint Suction Affected by labral Status
Manual Resistance Forearm Exercises
In this post, I wanted to show you guys some of the manual resistance drills we use @championptp on our shoulder and elbow clients, especially our baseball players. We love to use these drills because we can control so many variables with each athlete and tailor it for their specific needs.
We can control the speed and tempo, the direction of forces (eccentric, concentric), and the magnitude of the forces. Plus it’s a great way to interact with our clients. It’s also a great way to feel how well they’re progressing in their programs instead of just giving them dumbbells.
I have found these manual resistance drills to be very helpful with my overhead athletes and hope you give them a try on your clients soon! Let me know what you think or tag a friend below who may like to use these drills too.
In my course that I teach around the US, I try to include these concepts so you can practice and be able to utilize these drills for your clients…thanks!
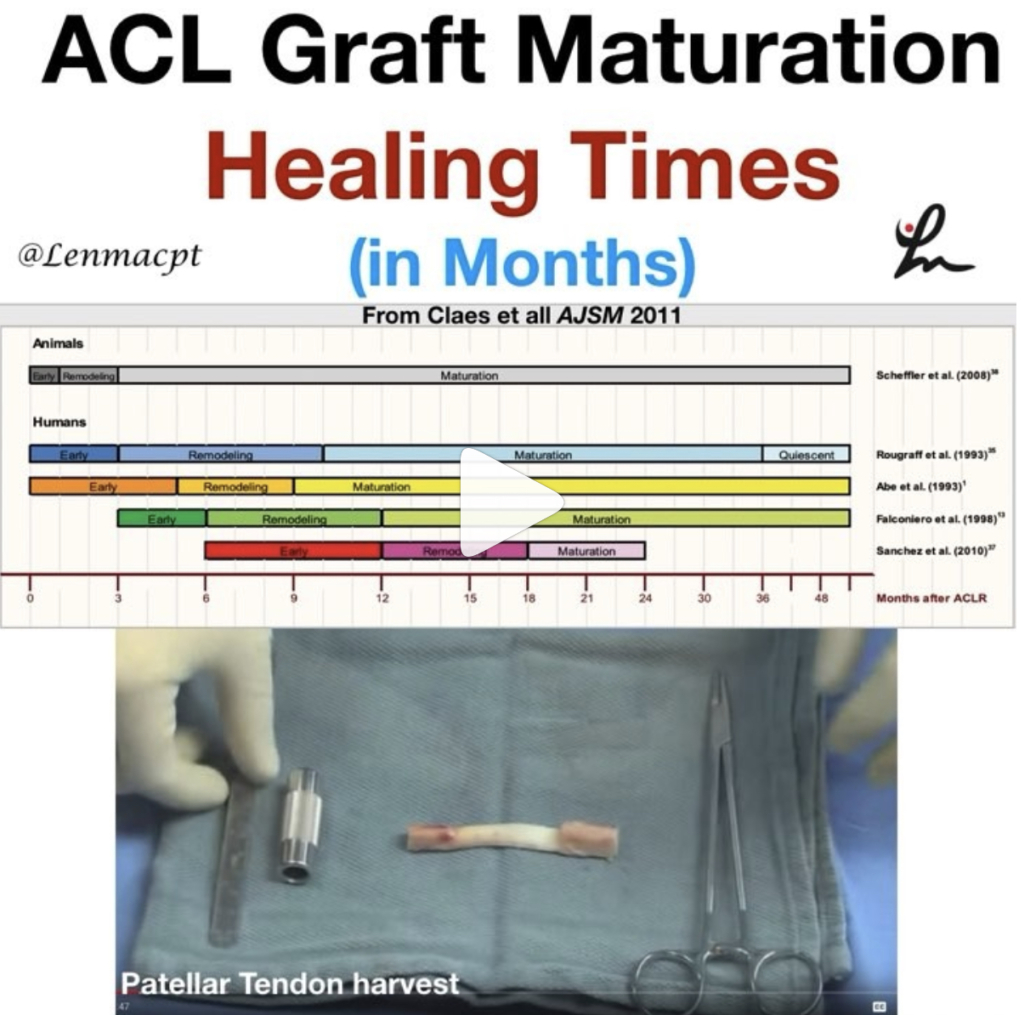
ACL Graft Harvesting and Healing times
In this post, I wanted to show some research studies on graft healing times and why we need to respect tissue biology.
The systematic review from AJSM 2011 looked at ‘The ‘‘Ligamentization’’ Process in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction.’
They essentially looked at 4 different biopsy studies on BPTB and Hamstring autograft reconstructions. They concluded that maturation of the graft, as determined by mainly vascularity and cellularity, was not complete until 12 months at the earliest. The healing time even extended to 24+ months as well.
The ligamentization endpoint is defined as the time point from which no further changes are witnessed in the remodeled grafts. The surgical procedure is quite involved, as you can see in the video that I took from @drlylecain on #YouTube.
As I’m rehabbing my clients, my decision making and post-op progressions often take into account:
✔️Healing biology
✔️Graft harvesting
✔️Graft Type
✔️Bone bruise presence (often!)
✔️Other concomitant issues (meniscus, articular cartilage).
So, respect the tissue and allow natural healing to occur before you add more exercises or are concerned that they’re not making the gains you’d expect.⠀
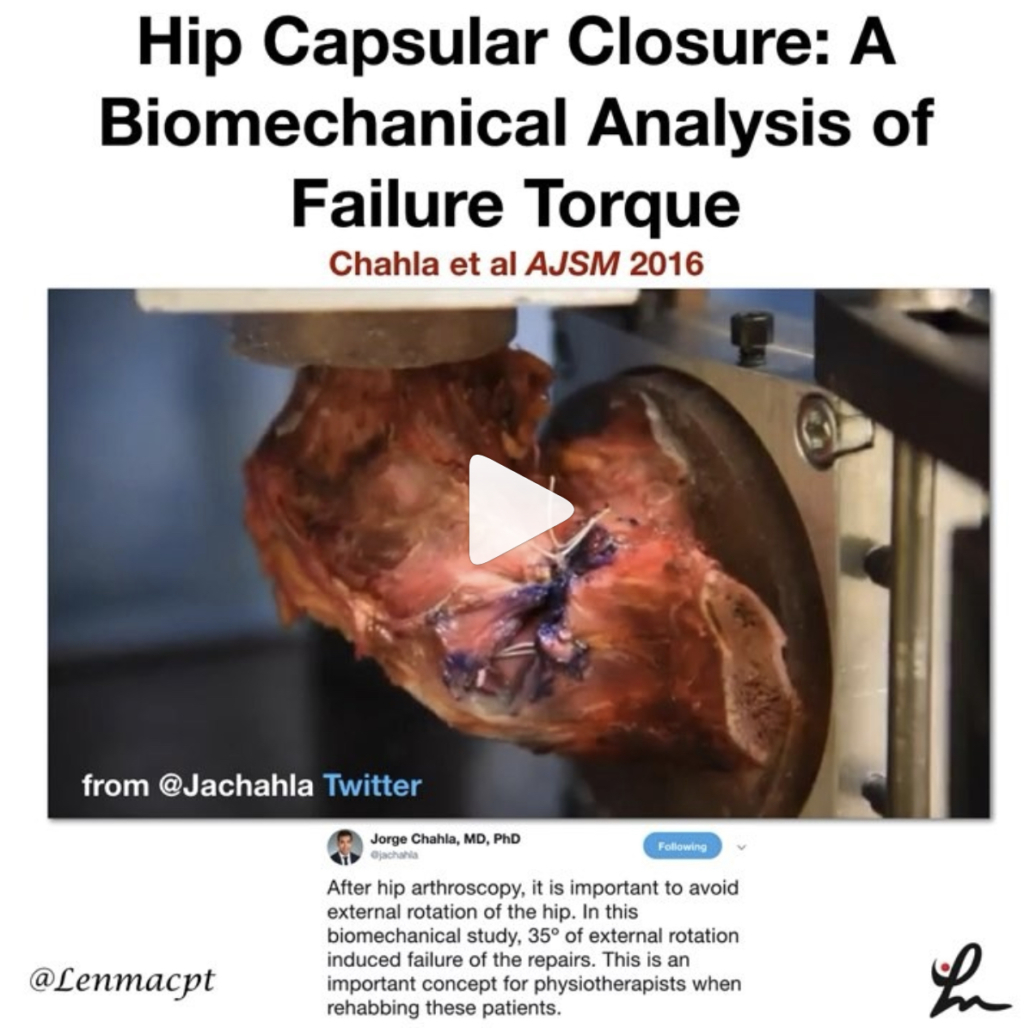
Hip Capsular Closure: A Biomechanical Analysis of Failure Torque
Chahla et al AJSM 2016
Interesting look at tissue failure, albeit in a cadaver graft, that should help to guide the physical therapist or ATC early in the rehab process after a hip scope.
The purpose of this study was to determine the failure torques of 1-, 2-, and 3-suture constructs for hip capsular closure to resist external rotation and extension.
The 3-suture construct withstood a significantly higher torque (91.7 Nm) than the 1-suture construct (67.4 Nm) but no significant difference was found between the 2- and 3- suture construct.
The hip external rotation degree in which the capsule failed was:
✅1-suture construct: 34 degrees
✅2-suture construct: 44.3 degrees
✅3-sutures: 30.3 degrees (yes, smaller than 2-suture construct)
I think as a #PT, we need to keep this study in mind and respect the healing tissues after a hip scope.
Love when we can get this information and put it into practice, similar to RTC repairs, ACL, etc.
Obviously, this was on a cadaver where there’s no guarding, pain or muscle contraction. We still need to know that there MAY be enough tension on the capsule to create potential issues (like tissue failure).
If you treat patients after hip scopes, then I recommend you read this cadaveric study.
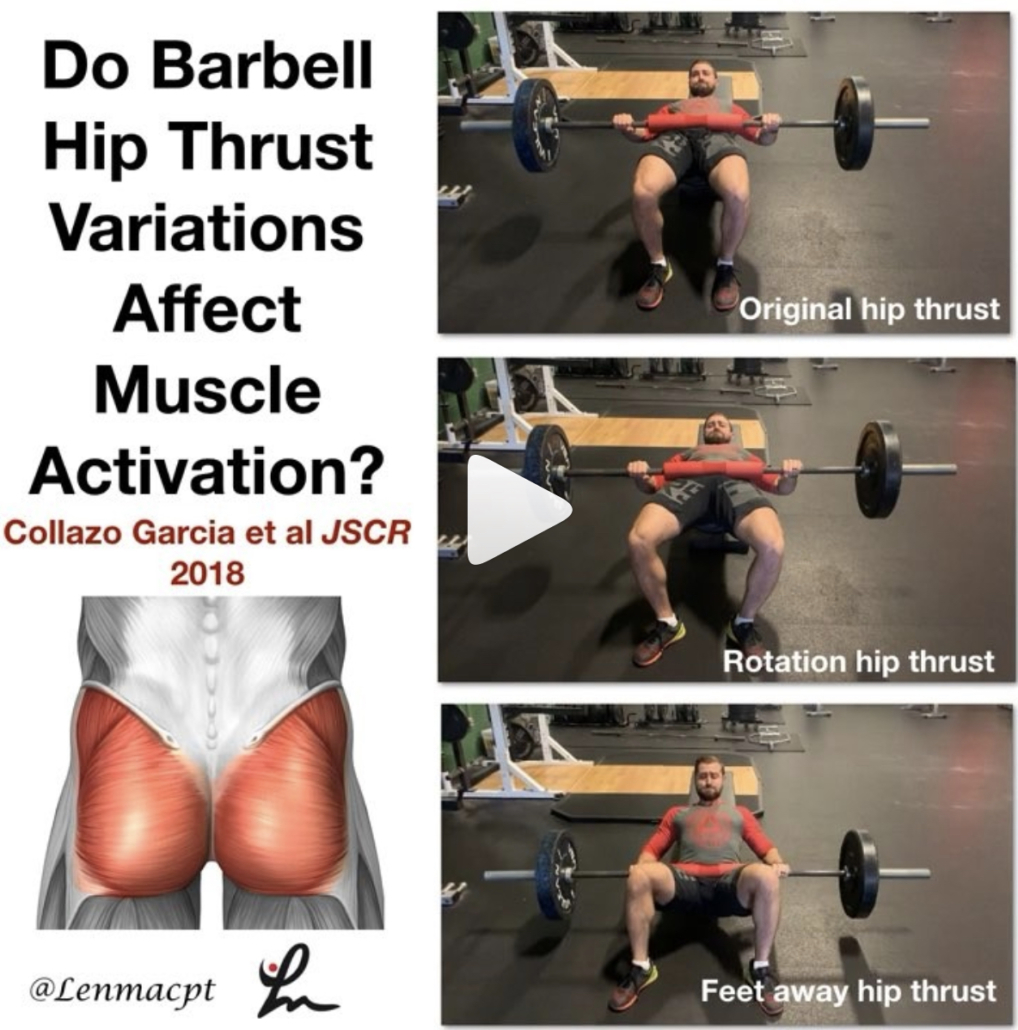
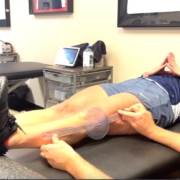
Barbell Hip Thrust Variations Affect Muscle Activation
COLLAZO GARCIA et al JSCR 2018
This study looked at the EMG activity of various lower body muscles while performing the hip thrust in various positions.
Their results showed that by varying the foot position into more external rotation, you can recruit the glute max and medius more than by the traditional hip thrust.⠀ …”the activity of the gluteus maximus increases significantly reaching up to 90% MVIC with only 40% of 1RM” with this hip ER variation.
Also, ‘when the distance between the feet is increased, the activity of knee flexors increases. Therefore, this is a very recommendable option to increase hamstring: quadriceps co-activation ratio.’
I like this study because it helps guide our rehab if we’re targeting a specific muscle group a bit more because of an injury or surgery.
It’s one of my go exercises for anyone with a lower body injury, especially after an ACL reconstruction. But I do use this exercise for most of my clients rehabbing from any injury, including the upper body.
It’s a great way to recruit the gluteus maximus and medius, which we know are hugely? (is that a word?) important to help produce and dissipate forces during athletic movements.
The exercise was widely researched by @bretcontreras1 and should be a staple in your rehab programs.
Check it out and add this to your go-to exercise list…thanks!
Hip Thrust Form
[REPOST] and a great one from @bretcontreras1 talking hip thrust form, which is perfectly coinciding with my post earlier today on variations to the hip thrust and how they affect muscle activation. Check out his original post below…highly recommended!
Teaching optimal hip thrust form is complicated. While the occasional lifter prefers and functions better staying fairly neutral in the head, neck, and spine, the vast majority of lifters do best maintaining a forward head position, which leads to ribs down and a posterior pelvic tilt.
It’s not just the forward eye gaze; the whole head has to maintain its forward position. You’re not hinging around the bench; the body mass above the bench stays relatively put, while the body mass below the bench is where the movement occurs.
The astute science geeks out there will rightfully point out that posterior pelvic tilt is associated with some lumbar flexion, and that lumbar flexion under load can be problematic. However, lumbar flexion is only dangerous when the discs are simultaneously subjected to compressive forces. With this style of hip thrust, the glutes are driving hip extension and posterior pelvic tilt, and erector spinae activation is greatly diminished. Core activation is what creates the bulk of the compressive forces, so with the erectors more “silenced,” the discs aren’t as compressed. This makes the exercise very safe. In fact, it’s safer than the “neutral” technique because as you rep to failure or go a bit too heavy, you will inevitably arch the chest and hyperextend the spine, which can lead to lower back pain.
We have 200 members at Glute Lab hip thrusting day in and day out, and there have been zero injuries to date. Considering how heavy we go, this is astounding.⠀
⠀
#gluteguy #glutelab #thethrustisamust⠀
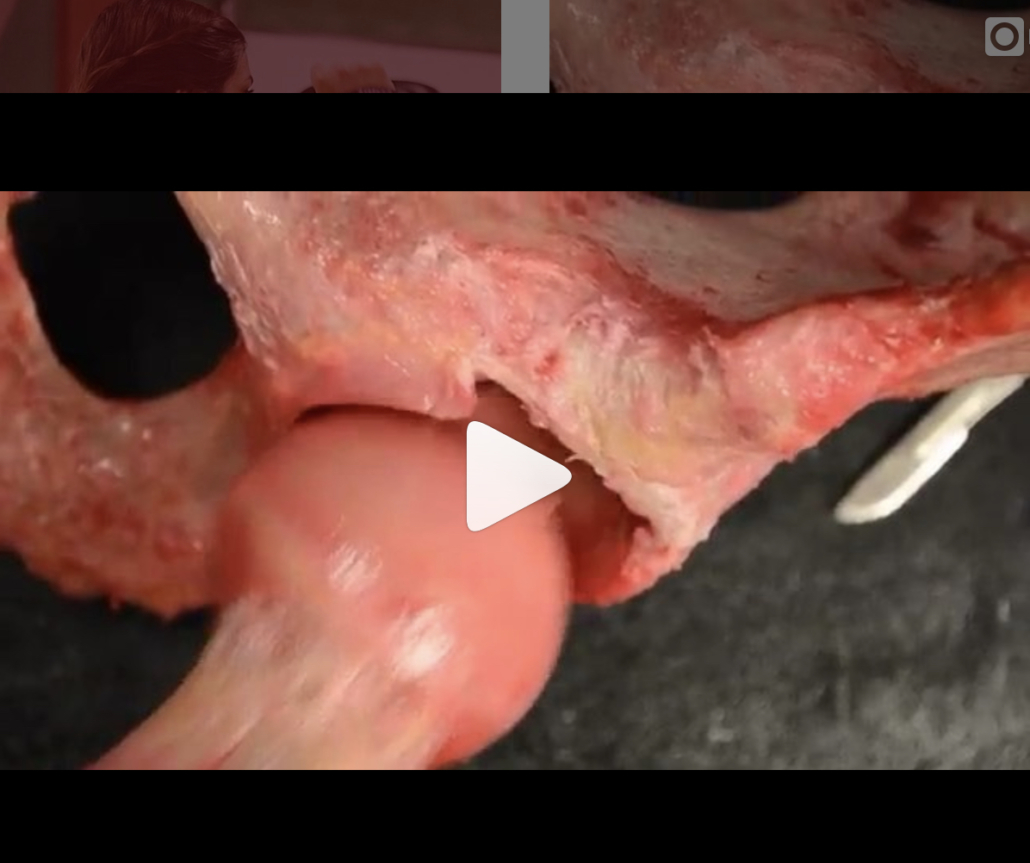
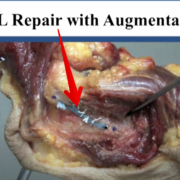
Hip Joint Suction and Stability
[REPOST] From @chicagosportsdoc and a very cool look at the suction within the hip joint that contributes to its stability. As the video progresses, they have simulated a labral tear that shows how easily the joint can dislocate. Once the labrum is repaired, the suction effect is recreated, and joint stability is re-established.
That’s 2 posts this week on the hip…if you want to see some awesome posts, then follow him. He just got on Instagram but his visual posts really aid in learning the mechanics of the various joints…see below!
An impressive demonstration of the powerful hip suction seal. When the hip labrum is injured, the seal is disrupted which can potentially produce microinstability. A labral reconstruction can restore the suction seal #labrum #sportsmedicine #hip #anatomy#orthopedicsurgery #medicine







 https://www.needpix.com/photo/230625/girl-soccer-kick-ball-youth-sport-game-kicking-football
https://www.needpix.com/photo/230625/girl-soccer-kick-ball-youth-sport-game-kicking-football

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!