The Week in Research Review, etc 10-22-18
That was a milestone week as my Instagram account finally hit 10k followers, whatever that means! I’ve really been pushing a daily post to help other rehab professionals better simplify the research. One milestone hit but I still want to keep publishing good quality research reviews. The Week in Research Review, etc 10-22-18 included:
- Do baseball Pitchers really have a tight posterior capsule?
- ACL strain curve during the squat
- Does the pec minor length influence shoulder pain?
- What does the literature say about the EMG activity of the rotator cuff, particularly of the supraspinatus, with ROM
- Classification of Meniscus Tears and Osteoarthritis
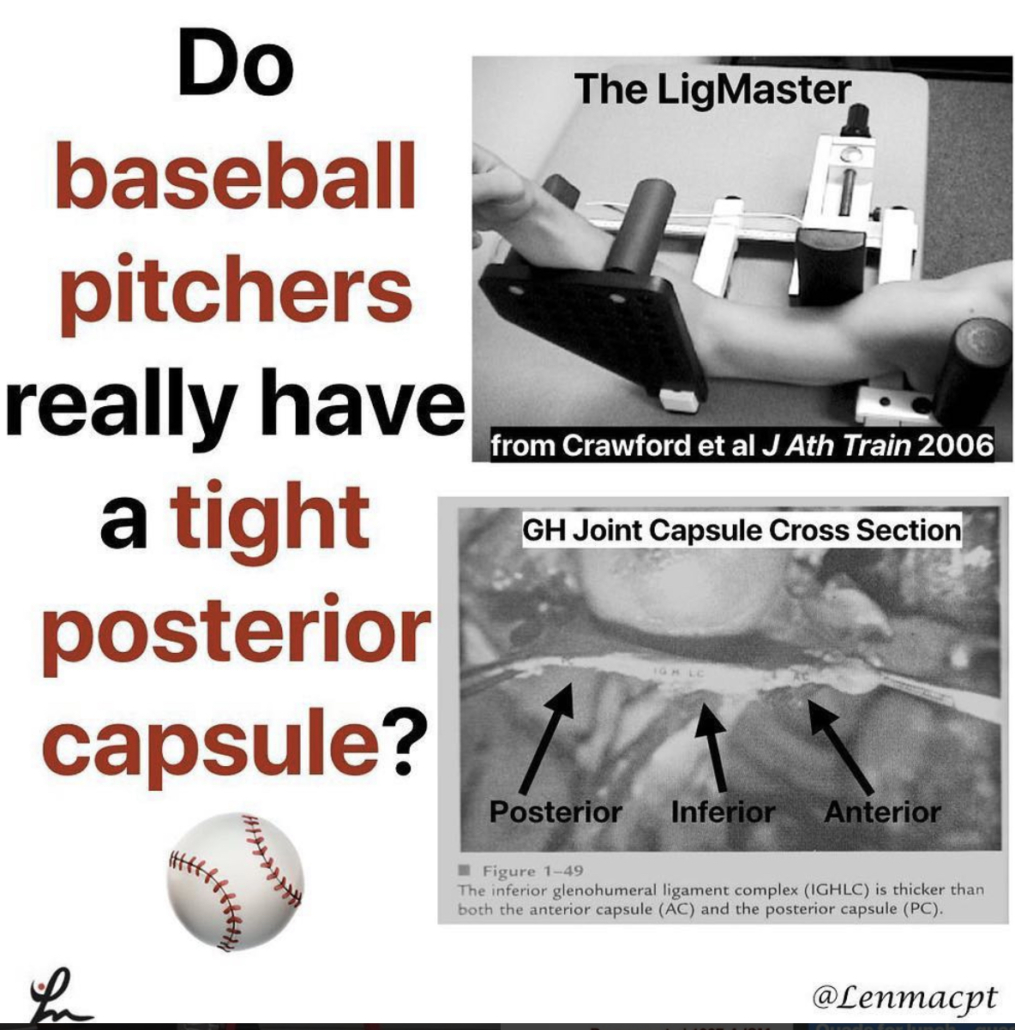
Do baseball Pitchers really have a tight posterior capsule?
My guess is emphatically no based on what I see on a daily basis, the general anatomy of the glenohumeral joint and some research studies.
Anatomy
1️⃣When I stretch a baseball pitcher’s shoulder, it is usually very mobile. I find this in both symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals.
If I try to assess their posterior capsule with a joint play technique, I can often translate the humeral head pretty far over the glenoid rim. Sometimes, I can even sublux the humerus!
2️⃣Anatomically, the posterior capsule is relatively thin compared to the anterior and inferior capsule (see the post).
In general, that capsule is thinner probably because of the glenoid position that is not strictly in the frontal plane.
Because of that, it is theorized that the capsule evolved to have less of a role in stabilizing the humerus.
3️⃣There are a couple of research studies that have specifically looked at baseball pitchers to determine their humeral head translation.
Borsa et al AJSM 2005 reported that posterior translation was actually greater than anterior translation in both the dominant and non-dominant shoulders of professional baseball pitchers.
Crawford et al J Ath Train 2006 found no significant differences in posterior glenohumeral laxity and stiffness between the throwing and non-throwing shoulders.
I understand why the theory exists and think it could be plausible but just don’t think it’s truly responsible for what we think.
We just don’t think we can stretch the posterior capsule with any joint mobilization or contract-relax procedure, including a sleeper stretch. I often giggle at all of those MD prescriptions that say ‘#GIRD, posterior capsule tightness’. I just treat what I find on my examination and ignore the script.
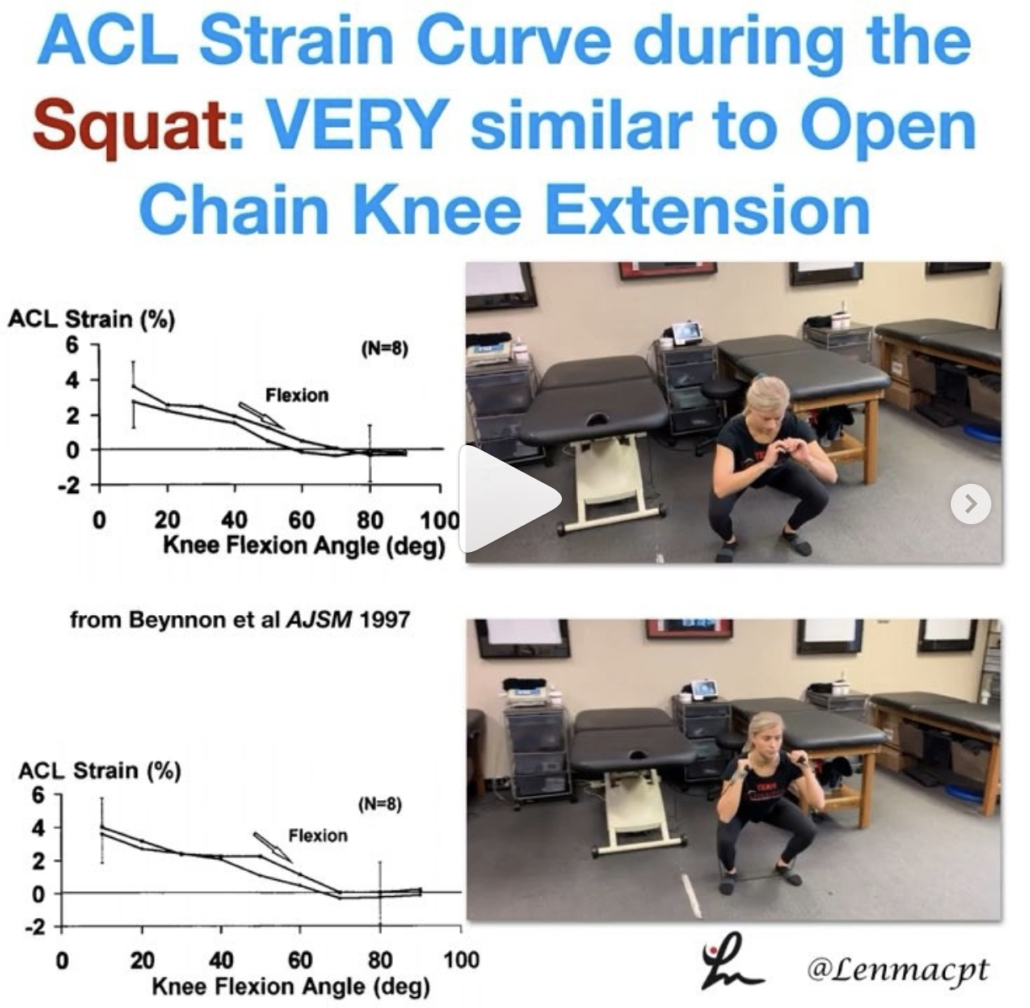
ACL strain curve during the squat
As you can see, the strain curve from the Beynnon et al study is very similar to the strain curve during resisted knee extension in a full ROM (90-0).
We argue all of the time about anterior tibial translation during the open chain exercises but often ignore the other side of the story.
The strain on the ligament is barely 4%, which is in line with many functional activities like walking, descending steps, etc. The argument that we’re going to stretch the ligament out just has not been proven in the literature.
I wanted to show the closed chain strain curve so you could compare it to the open chain strain curve. I know the n=8 argument is present but we really don’t have much more data on the ligament in vivo that shows the true effects of open vs closed chain exercises on the ACL.
Again, as @barbhoogie mentioned, you need to monitor the PF joint, especially after a patella tendon autograft but as long as we’re not aggravating that joint, then I begin early 90-0’s and mini squats as tolerated.
Do you agree with this? Do you prevent squats early on during the ACL rehab process? If you don’t, then why do you hold back on full active knee extension exercises?
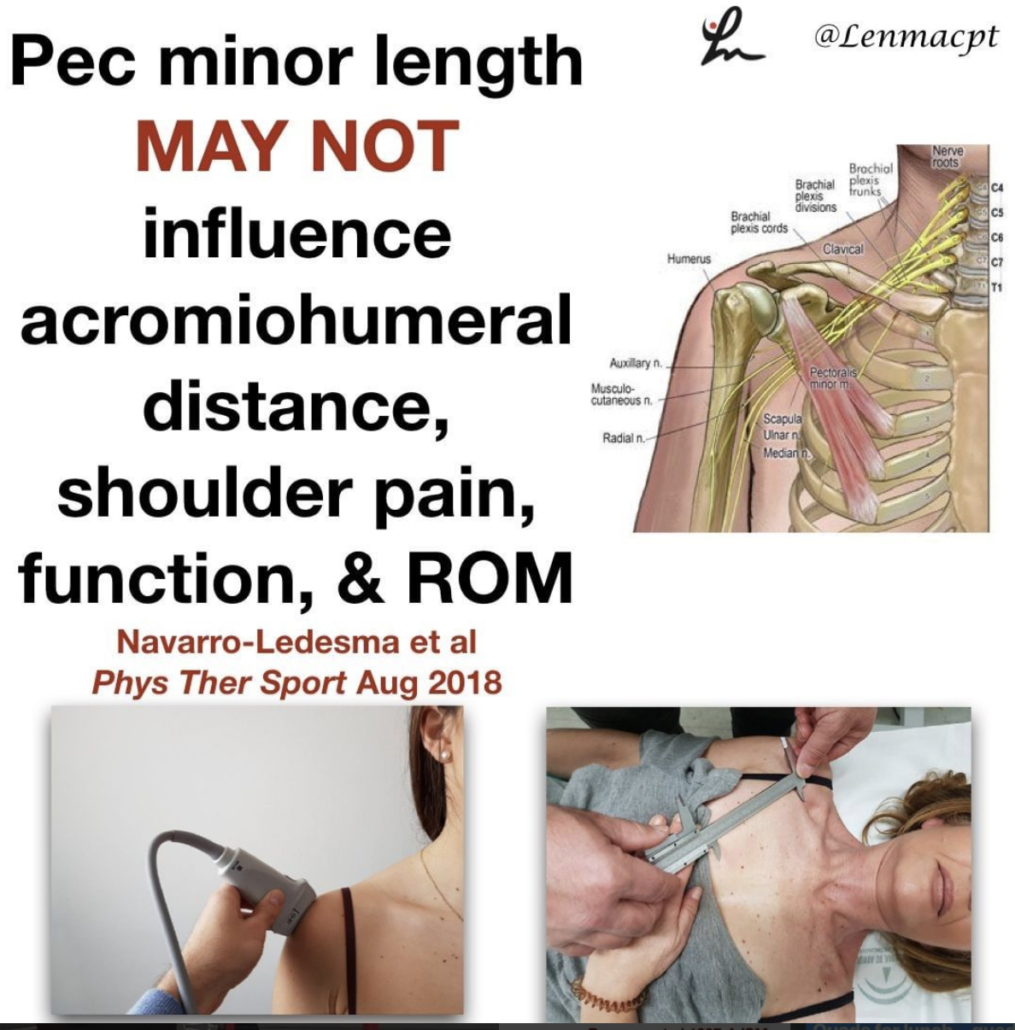
Does the pec minor length influence shoulder pain
Does the pectoralis minor length influence acromiohumeral distance, shoulder pain-function, and range of movement? Navarro-Ledesma et al Phys Ther Sport Aug 2018.
Their conclusion: Pectoralis minor length is not a distinguishing factor in shoulder⠀
assessment when a chronic condition exists, and it seems not to play a key role in pain perception and ROM.
54 participants with chronic shoulder pain in their dominant arm were recruited, as well as fifty-four participants with a pain-free shoulder.
The resting muscle length is measured between the caudal edge of the 4th rib to the inferomedial aspect of the coracoid process with a sliding caliper.
The acromiohumeral distance (AHD) was defined as the shortest linear distance between the most inferior aspect of the acromion and the adjacent humeral head, measured by ultrasound.
An interesting study that used an asymptomatic control group along with the contralateral shoulder of the symptomatic subject. A pretty clean study that is very interesting. I’m not going to say that the pec minor doesn’t play a role in shoulder pain but maybe its role is not as prominent as we think.
What do you think? Do you find pec minor length has a substantial role in your patients with shoulder pain?⠀
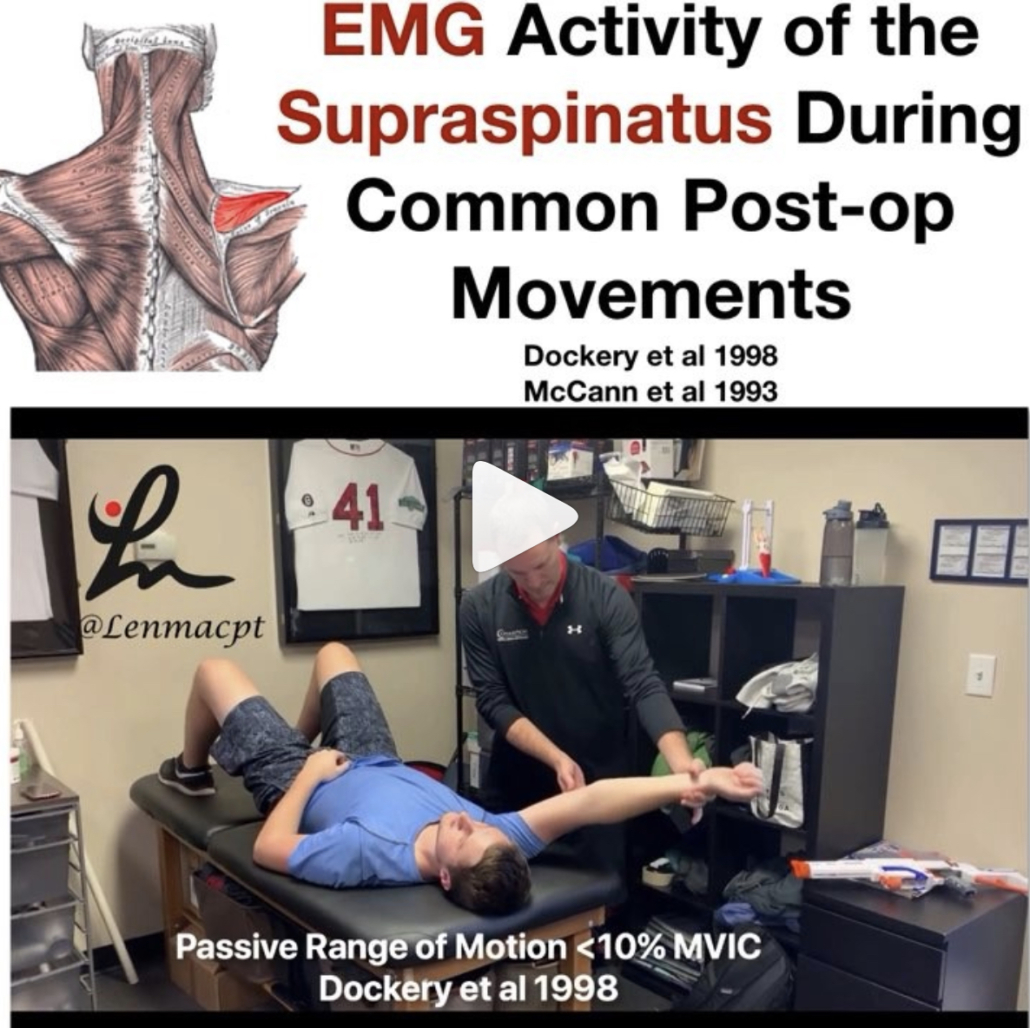
EMG of the rotator cuff during rehab exercises
What does the literature say about the EMG activity of the rotator cuff, particularly of the supraspinatus, with ROM?
Many PT’s and doctors are uncertain when to safely begin physical therapy after a shoulder surgery, particularly after a rotator cuff repair. In my 15+ years as a PT, I’ve seen docs begin PT post-op day 1 or wait as long as 6 weeks (which drives me bonkers!!)
In this snippet that I’ve taken from an upcoming blog post at LennyMacrina.com. I discuss the research that’s helping to guide best practice, in particular, the research that looks at PROM and AAROM and how much EMG activity is actually going on in the supraspinatus with each movement.
As you can see in the video, there’s minimal supraspinatus activity (<20% is considered minimal) for all motions. Keep in mind, many of these studies are done on healthy individuals but who in their right mind would volunteer their newly repaired RTC repair to have fine-wire EMG done on them?
So, I can only draw my conclusions from a limited body of evidence and my own anecdotal evidence (which consists of 12+ years of immediate PROM POD 1). Many still think it’s safe to get a RTC repair patient’s shoulder moving early for many reasons that I will describe in this blog post.
I just wanted to get this early point out there to get another discussion going. I think our patients can do much better after a RTC repair and this is one of the reasons.
Do you agree? Do you advocate for early PROM after a RTC repair, especially a small-medium repair?
Classification of Meniscus Tears and Osteoarthritis
Great post by @physicaltherapyresearch talking about the various types of meniscus tears. Nice visual & description of each type and the incidence of OA. Take a look! 👇🏼
_______________
Meniscus Tears and Osteoarthritis
💡
Prevalence of meniscal tears is estimated as ~24-31% of some populations, increasing with age and ranging from 19% in women aged 50–59 years to 56% among men between 70 and 90 years and is markedly higher in established OA subjects.
💡
Medial meniscus and/or the posterior horn tears make up 66% of cases, with horizontal and complex tears being the most common.
💡
Most subjects with a meniscal tear are asymptomatic.
💡
Regardless of morphologic type, meniscal tears are strongly associated with OA cross-sectionally and predict OA longitudinally and are considered to be part of the spectrum of early or pre-radiographic disease
📝📝📝
TEAR TYPES INFO:
Often enough, meniscal tear types are categorized into varying groups for comparison rather than separately compared to each other.
📝
There is a striking lack of data on the relevance of different morphologic types of meniscal tears in OA.
📝
Horizontal and complex tears are common findings in knees with OA
📝
Posterior radial tears of the medial meniscus are associated with a high degree of cartilage loss and meniscal extrusion, and appear to be a highly relevant event in the progression of OA in the knee. 📝
Lateral meniscus radial tears affect younger individuals and are considered post-traumatic.
📝
Despite their suggested high relevance, radial tears are more commonly misdiagnosed on MRI than any other type of tear.
📝
While medial meniscus posterior root tears are of “radial” morphology, there is growing interest in regarding them as a separate entity.
📝
Longitudinal and bucket handle tears affect younger individuals and are highly associated with ACL injuries, favoring a traumatic etiology.
📝
MRI is important to detect and locate a possible displaced tear.
📝
Further epidemiologic studies should focus on the morphology of specific meniscal tears to better understand their relevance in the genesis and progression of knee OA.
📚📚📚
SOURCE:
Jarraya et al. 2017 Semin Arthritis Rheum










Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!