Another week of some great discussions and learning opportunities. The Week in Research Review included:
- Risk Factors for Patellofemoral pain
- Shoulder ROM and elbow injuries
- Rotator Cuff Exercises
- Eccentric or Concentric exercise for Tendinopathy
- Hamstrings Protect the ACL
- Stretching the Shoulder in the Overhead Athlete
Share with your friends and have them subscribe to the weekly newsletter!

Risk factors for patellofemoral pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis Neal et al BJSM 2018.
This systematic review and meta-analysis of 18 studies involved 4818 participants, of whom 483 developed patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS).
First off, PFPS is a wastebasket term that basically tells the client that they have knee pain…that’s it.
My 1st job is to educate the client about this fancy term because they often come in confused and wanting more information.
I use a good subjective exam to have the patient help me narrow in on a potential cause so I can answer the question ‘why’.
My clinical exam will attempt to diagnose the particular culprit…whether it’s mechanical, overuse or something else.
Back to the study…it showed that in patients with PFPS, quadriceps weakness in military recruits and higher hip strength in adolescents were risk factors for PFP.
Not surprised by the quadriceps weakness but kinda surprised by the hip weakness!
The same authors showed this in JOSPT 2012 Lankhorst et al that weaker knee extension strength, expressed by peak torque, appears to be a risk factor for PFPS.
Not sure what to do with the hip strength as a risk factor in adolescents but maybe it becomes a biomechanical issue if the hips are stronger than the quadriceps, relatively.
Do you guys see this out there as well? The key, as usual, is to strengthen the quadriceps!
I would also say activity modification that is causing the quad weakness (overuse) and a progressive return to their activity.
Chime in and let’s talk this out…thanks!⠀

Deficits in glenohumeral passive range of motion increase risk of elbow injury in professional baseball pitchers: a prospective study. @wilk_Kevin, Macrina et al AJSM 2014.
In this paper, we looked to determine whether decreased ROM of the throwing shoulder is correlated with the onset of elbow injuries in professional baseball pitchers.
This one took years to get all of the data collected through multiple spring training trips to the @raysbaseball facilities.
In the end, we were able to show that: ⚾️pitchers with deficits of >5° in total rotation in their throwing shoulders had a 2.6x greater risk for injury.
⚾️Pitchers with deficit of ≥ 5° in flexion of the throwing shoulder had a 2.8x greater risk for injury.
These findings have guided our evaluation and treatment strategies at @championptp.
We hypothesize that loss of flexion may be a result of some soft tissue limitation of the lats, teres, pecs and other muscles.
We focus much of our attention on these muscle groups during our arm care to help regain the flexion and may even help gain back some of the ER in those that are tighter than normal…whatever that means.
After soft tissue work, we look to work on dynamic stability and strength in the newly gained ROM.
Do you use these similar concepts with your baseball pitchers too? Tag a friend who may be interested in this study…thanks!⠀

Rotator Cuff Exercises
In this post, I wanted to discuss my go-to exercises for the shoulder when someone presents with an injury or pain.
Of course, my exam TRIES to determine the tissue involved but most of our clinical exam tests cannot pinpoint the exact pain generator and pathological tissue.
With that, I have certain exercises that I think, through the available EMG data, are the best to help regain strength and confidence prior to beginning their return to sport (or life) activities.
Numerous studies have looked at the EMG during these specific motions and have determined that the supraspinatus and infraspinatus have higher relative levels compared to other positions, say the full can vs empty can debate, for example.
Take a look at these classic studies to help guide your programs:⠀
❇️Blackburn et al JAT 1990
❇️Townsend et al AJSM 1991
❇️Reinold et al JOSPT 2002
❇️Reinold et al JAT 2007
❇️Kelly et al AJSM 1996
❇️Worrell et al Med Sci Sports Exerc 1992
❇️Jobe et al 1982
❇️Decker et al AJSM 2003
These papers have provided the foundation for today’s shoulder programs and are some that I discuss during my Biomechanics lectures that I give when teaching my course.
Are you familiar with these papers and do you keep them in mind when building your shoulder programs for your clients?
Tag a colleague or friend that may want to see this post…thanks!⠀

Eccentric or Concentric Exercises for the Treatment of Tendinopathies? Couppe et al JOSPT Nov 2015
Interesting clinical commentary from a few years ago talking about tendinopathy treatments.
Most PT’s and ATC’s generally talk about eccentric loading of tendons to help treat suspected tendon pain.
In this review, they discuss the potential mechanisms that may aid in helping people suffering from tendon pain.
I found this statement very interesting:
👉🏼”There is little evidence for isolating the eccentric component of a loading-based regime.
👉🏼The basic mechanisms that are likely to influence tendon adaptations appear to be related mainly to tendon load/strain magnitude and duration, and there is no theoretical basis for greater tendon loads in eccentric exercises at a given force (body weight or external load).” 🤯
As always, it makes me think that as specific as we think we are with some of our exercises, maybe just putting any strain through the muscle-tendon unit is good enough.
Have you guys read this review? What do you think? is this similar to what you see in your practice?
Tag a friend who may want to read or comment on this post…thanks!⠀
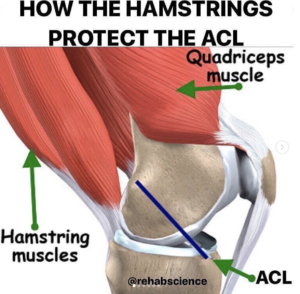
𝐇𝐚𝐦𝐬𝐭𝐫𝐢𝐧𝐠𝐬 & 𝐓𝐡𝐞 𝐀𝐂𝐋
Great post by @rehabscience talking about the influence of the hamstrings on the #ACL. A big focus of my rehab for my patients that have had an ACL reconstruction involves building hamstring strength.
Check out his original post below!
💥𝐇𝐚𝐦𝐬𝐭𝐫𝐢𝐧𝐠𝐬 & 𝐓𝐡𝐞 𝐀𝐂𝐋💥
———–
📌The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is an extremely important ligament in terms of overall knee integrity and stability. Specifically, the ACL connects the femur (thigh bone) to the tibia (shin bone) and runs at an oblique angle from the posterior aspect of the femur to the anterior aspect of the tibia. Due to this arrangement, the ACL is responsible for preventing anterior translation of the tibia or posterior translation of the femur.
–
🔎Now, many of us are aware of the importance of the quadriceps to knee health, but, often times, the hamstrings get neglected. The hamstrings run along the posterior (backside) of the thigh and insert onto the posterior surfaces of the tibia and fibula (shin bones).
When contracting, the hamstrings work to bend the knee, but also pull the tibia posteriorly. In this way, the hamstrings can serve as a dynamic protector of the ACL by limiting excessive anterior displacement of the tibia and strain on the ligament.
–
✅If you are looking to reduce your risk of ACL injury or recovering from an ACL reconstruction, don’t forget to include hamstring work in your strength training program as this group has an instrumental role in protecting the ACL.
–
⬅️Swipe left to see several exercises from myself, @jasonbombard, @zerenpt and @strengthcoachtherapy that can be incorporated to increase hamstring strength.
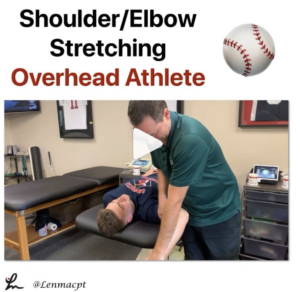
⚾️Stretching the Overhead Athlete ⚾️
In this post, I wanted to give a glimpse into the stretching routine I use on some of my OH athletes before and after a workout, bullpen or a game.
I like to stretch the shoulder into external rotation to make sure the athlete can maintain that important ROM, especially to keep that layback or late cocking position.
I also like to work on horizontal adduction with the lateral border of the scapula stabilized. It’s important that the athlete feels the stretch in the back of the shoulder and nowhere close to the front of the shoulder.
This is the lone reason why I have gone away from the sleeper stretch and focus on horizontal adduction.
I also stretch out the forearm flexors by extending the elbow/wrist and all of the fingers, including the thumb (don’t forget about the thumb!)
I also like to stretch the shoulder joint into flexion by pinning down the scapula and hope I’m somewhere on the lats and/or subscapularis to be able to stretch these muscles out and improve that overhead position.
Remember, in 2014 we showed a loss of flexion increased the risk of medial elbow injuries by almost 3x.
I like to repeat the process a few times until I feel like we maximized the amount of new ROM.⠀
.⠀
At the same time, we’re chatting about the session, how it went, what’s to come, how their fantasy football team is doing, etc.
It’s my way to connect with each client before and after they have a session with me. I feel this is very important and often overlooked by other PT’s.
Do you have any other stretches you like to do? Tag a friend who may want to check out this video…thanks!⠀