This week I posted a lot of research and thoughts on shoulder and knee rehab, particularly after an ACL injury. I also shared some others posts that really complimented my posts so there’s some bonus reading to do too. Hope The Physical Therapy Week in Research Review helps your Monday patients and beyond! Take a read and share with your friends!
- Co-morbidities in the first 2 years after arthroscopic hip surgery: substantial increases in mental health disorders, chronic pain, substance abuse, and cardiometabolic conditions. Rhon et al BJSM 2018.⠀
- Range of Extension Correlates with Posterior Capsule Length after Knee Remobilization Zhou et al Med Sci Sports Exerc 2018⠀
- Sidelying External Rotation- The 1 exercise in all upper body programs
- @dr.jacob.harden talking Infraspinatus release.
- Do you account for Bone Bruises after an ACL
- @cbutlersportspton bone bruises and the specifics
- When is it safe to initiate full AROM knee extension after an ACL-PTG autograft
- @mickhughes.physio on when it MAY be safe to initiate full knee extension from 90-0 after an ACL reconstruction.

Comorbidities after Hip Arthroscopy
Co-morbidities in the first 2 years after arthroscopic hip surgery: substantial increases in mental health disorders, chronic pain, substance abuse and cardiometabolic conditions. Rhon et al BJSM 2018.
This is an interesting study on 1870 mainly US Military personnel between 2004-13 (~33% were not active duty).
Relative to baseline, cases of:
❇️mental health disorders rose 84%
❇️chronic pain diagnoses increased by 166%
❇️substance abuse disorders rose 57%
❇️cardiovascular disorders rose by 71%
❇️metabolic syndrome cases rose by 85.9%
❇️systemic arthropathy rose 132%
❇️sleep disorders rose 111%
The comorbidity with the greatest increase of new cases was that of mental health disorders (26% of the entire cohort). Age and socioeconomic status had significant associations on outcomes as well.
Just an eye-opening study that followed each subject 2 years after their respective surgeries. One giant variable that jumped out at me was that they used mainly military personnel only as the subjects.
We certainly can’t extrapolate on non-military personnel but need to keep this study in mind for others treating a similar cohort. Did the surgery cause these disorders? Absolutely not! No causation can be associated and that is very important!
What do you think about this study and how mainly military personnel and civilians that were tracked ending up developing many chronic disorders? I say it is very troubling! Let’s chat…and remember, this is not a causation study but just a reminder to educate and monitor your patients’ well-being after a surgery.
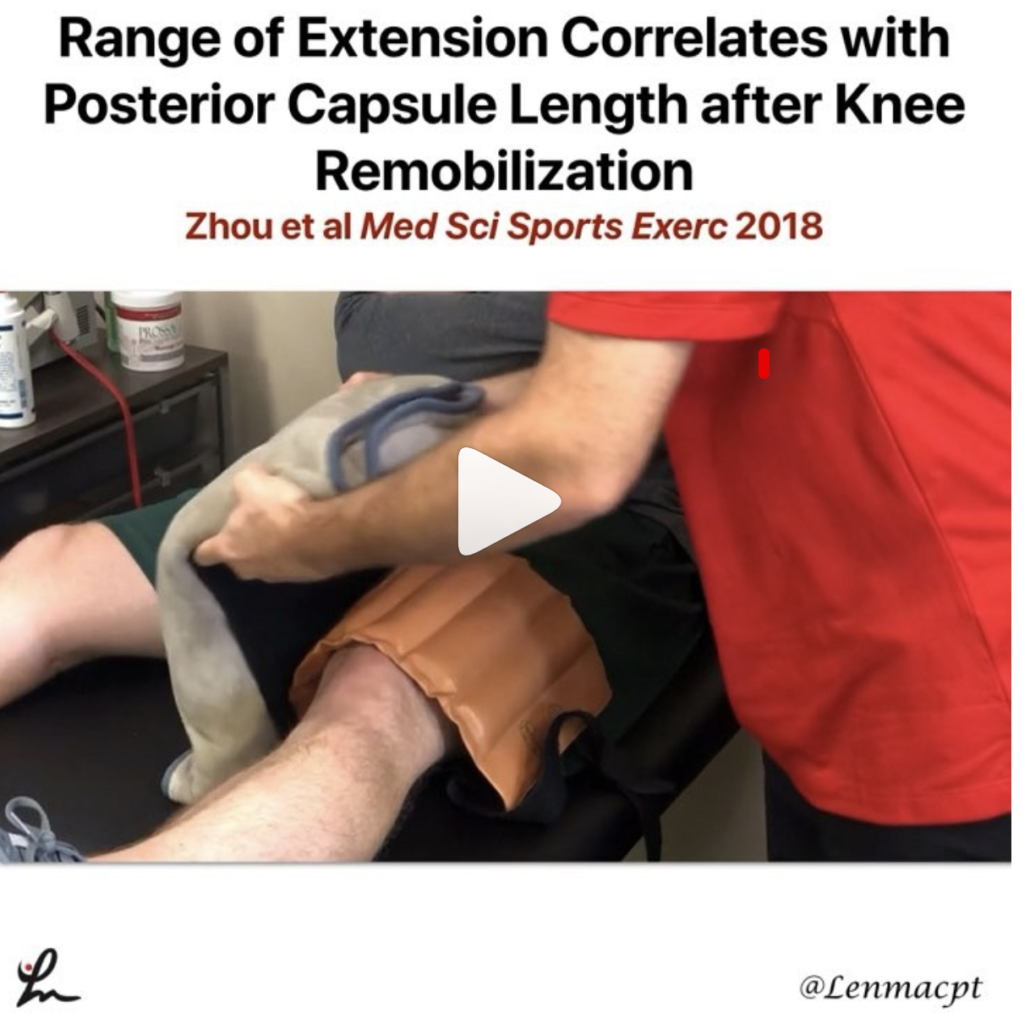
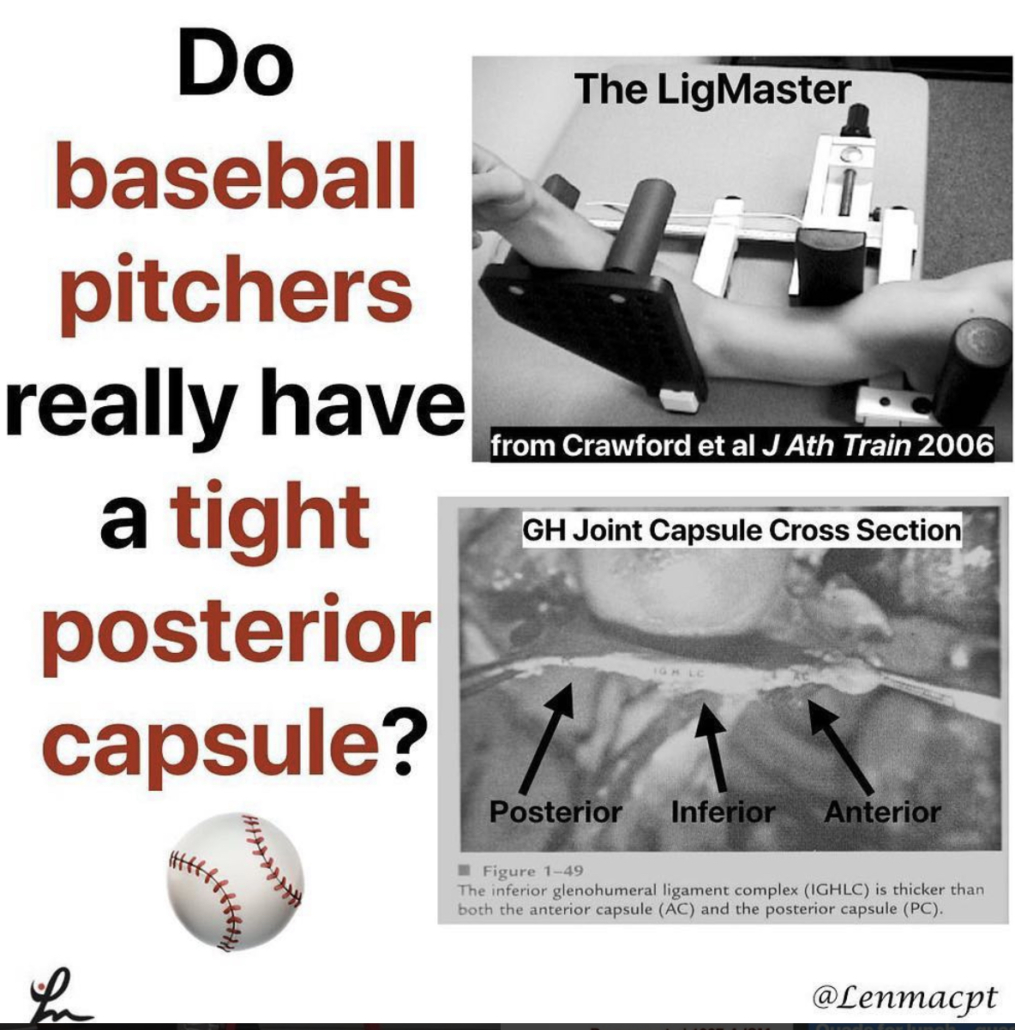
Posterior Capsule Limits Knee Extension after an ACL
Range of Extension Correlates with Posterior Capsule Length after Knee Remobilization Zhou et al Med Sci Sports Exerc 2018
This study is a confirmation bias for me because it showed that the knee’s posterior capsule limits extension after immobilization (in rats!) This is why I’m a huge proponent of low load long duration stretching of most joints when they begin to get stiff.
It seems as if the prolonged stretching is needed to regain collagen length and return the ROM. I know it’s in rats so calm down…but we need to get the data from somewhere.
Take it with a grain of salt but know that LLLD is going to be the best mode to return ROM (and not just hamstring stretching).⠀
.⠀
Do you agree? Do you treat rats with stiff knees? Then this study was created for you!

The Best Exercise for the Rotator Cuff
❗️Sidelying External Rotation- The 1 exercise in all upper body programs❗️
I really think this exercise should be in everyone’s program, whether going through rehab for a painful shoulder or a high level, healthy powerlifter. The role of the infraspinatus and other rotator cuff muscles is crucial to maintaining humeral head stability.
Sidelying external rotation has been shown to elicit the highest amount of EMG activity for the infraspinatus so I give this exercise to everyone, once there are no precautions for tissue healing. The infraspinatus and subscapularis (front rotator cuff muscle) are force couples that help to stabilize the humerus within the glenoid. Weakness of the infraspinatus may affect this force couple and create an inefficient movement within the joint.
My goal for all of my clients is to create an efficient movement that allows them to work at their highest level. The infraspinatus is a critical muscle of the shoulder complex so MOST of my programs include this exercise.

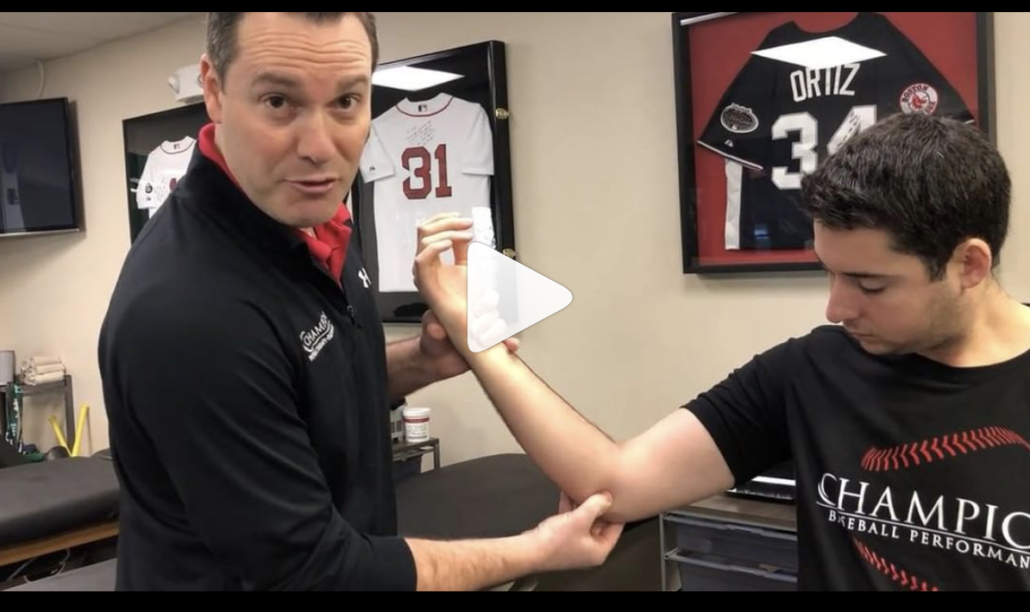
Myofascial Release of the Infraspinatus
Great post by @dr.jacob.harden talking Infraspinatus release. Perfect timing for my earlier post today looking at my go to exercise for the shoulder joint. Check his post out below!👉🏻 🔴 𝙃𝙊𝙒 𝙏𝙊 𝙍𝙀𝙇𝙀𝘼𝙎𝙀 𝙄𝙉𝙁𝙍𝘼𝙎𝙋𝙄𝙉𝘼𝙏𝙐𝙎
Coming at ya with a little #throwbackthursday since I’m about to jump on a plane across the pond to London. So we’re looking at how to do a pin and stretch for the rotator cuff, specifically the infraspinatus. The infraspinatus is the main external rotator of your shoulder, so it’s that muscle we see everyone working when they swing there 5 pound plates side to side in their warm-ups. (Side note: if you do that, please use a band or do it sidelying. Standing with plates does nothing but work the bicep.👍)
This can also help with some those little hypersensitive areas in the back of the shoulder. If you’re feeling those spots or having shoulder pain or just want to improve your internal rotation a bit, this release can help.
𝗛𝗲𝗿𝗲’𝘀 𝗵𝗼𝘄 𝘁𝗼 𝗱𝗼 𝗶𝘁:
🔹️Ball placement is below the spine of the scapula.
🔹️Internally rotate, flex, and adduct the shoulder
🔹️Work back and forth for a minute or so
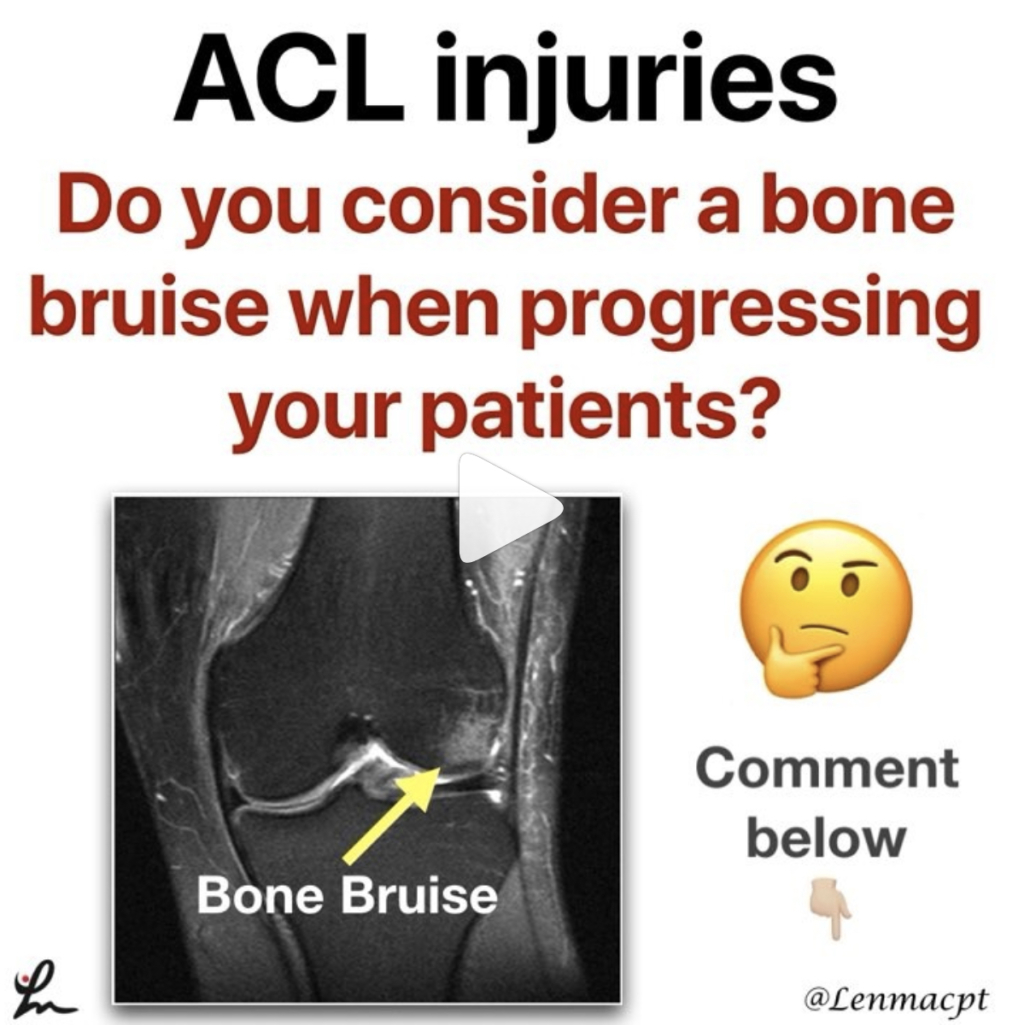
Bone Bruises after an ACL
Do you even consider a bone bruise after an ACL when progressing your patients? I know I certainly do and one of the major reasons why I have gone a bit slower with my latter stage progression, especially to impact activities like plyometrics and running.
There are a few studies that have shown the presence of a bone bruise after an ACL injury but we are not 100% certain this eventually leads to joint degradation.
Hanypsiak et al included 44 patients (82%) who underwent unilateral ACLR without multi-ligament involvement. Thirty-six (82%) patients had a bone bruise on index MRI. Potter et al reported all patients in their cohort sustained chondral damage at the time of injury.
Faber et al examined 23 patients with occult osteochondral lesion (bone bruise) who underwent ACLR. They found that at 6-year follow-up, a significant number of patients had evidence of cartilage thinning adjacent to the site of the initial osteochondral lesion (13/23 patients).
So as you can see, bone bruises are more common than most people think. This may be one reason why osteoarthritis rates are much higher in ACL reconstructed knees.
Additional factors, such as cartilage and meniscus injury, associated with ACL rupture may play an important role in subsequent outcomes following surgical reconstruction independent of a bone bruise.
Do you consider a bone bruise when progressing your patients back from a knee injury like an ACL reconstruction?
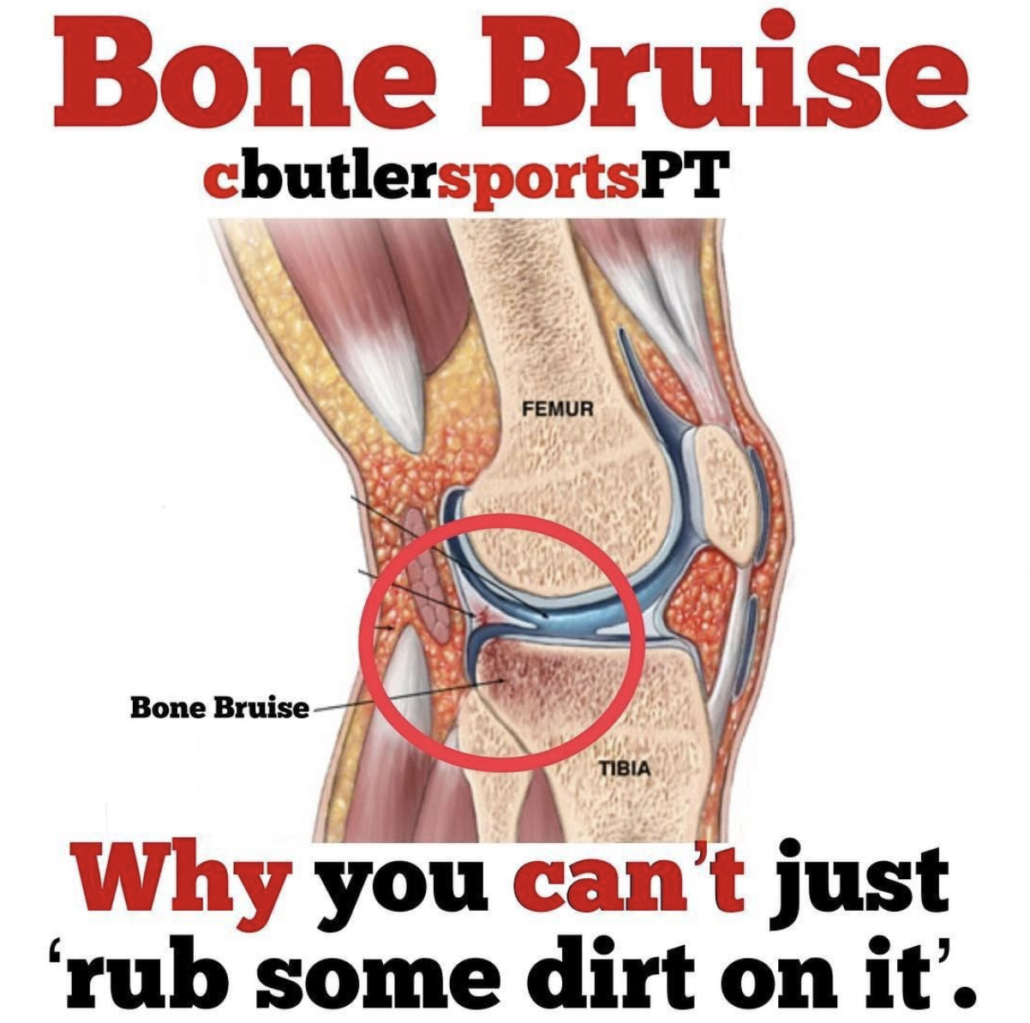
Types of Bone Bruises after an ACL Injury
@cbutlersportspton bone bruises, which fits perfectly with my post earlier today. He talks about the 3 different types of common bone bruises…check it out below!
❗️What is a Bone Bruise❗️We often hear that one of our Fantasy Football players has a Bone Bruise and may be out for a few weeks.
It sounds like something that an NFL athlete should be able to tough out, right?
Here’s why you may need to put in a backup for a few games.
A bone bruise occurs when several trabeculae in the bone are broken, whereas a fracture occurs when all the trabeculae in one area have broken. Trabecular bone is also known as spongy bone.
—-Three Types of Bone Bruises—-⠀
1️⃣Subperiosteal hematoma: A bruise that occurs due to an impact on the periosteum that leads to pooling of blood in the region.⠀
2️⃣Intraosseous Bruising: The bruise occurs in the bone marrow and is due to high impact stress on the bone.⠀
3️⃣Subchondral Bruise: This bruise is bleeding between cartilage and bone such as in a joint.
—-Symptoms of Bone Bruises—-
•Pain and tenderness in the region of injury
•Swelling in the region of injury
•Skin discoloration in the region of injury
Bone bruises often occur with joint injuries, such as ankle sprains and ACL tears, therefore a bone bruise can also coincide with stiffness and swelling in the joint.⠀

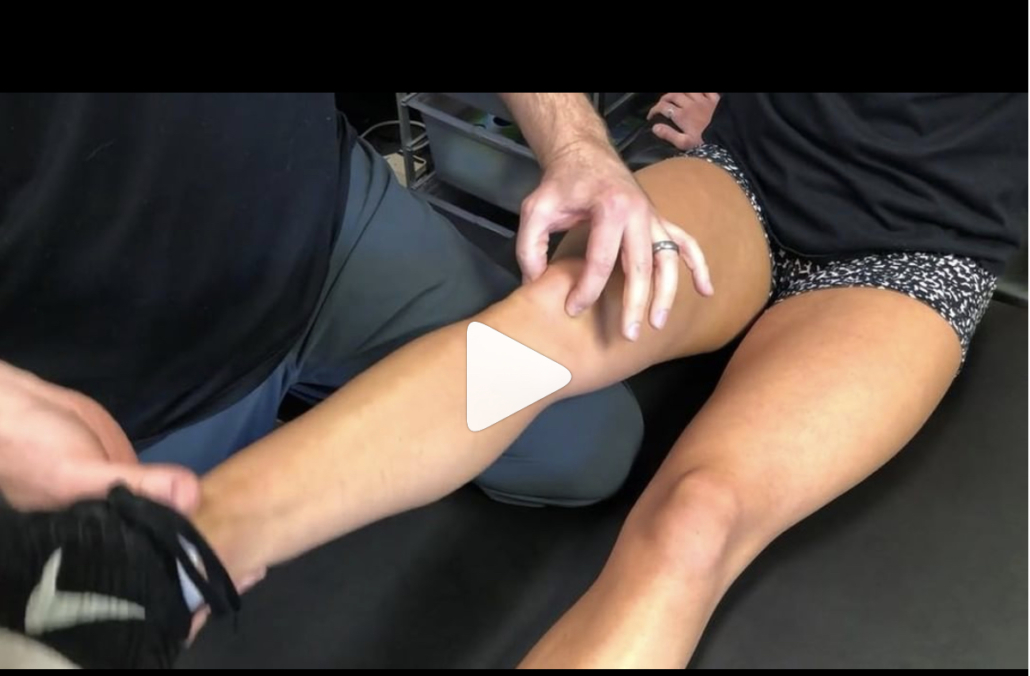
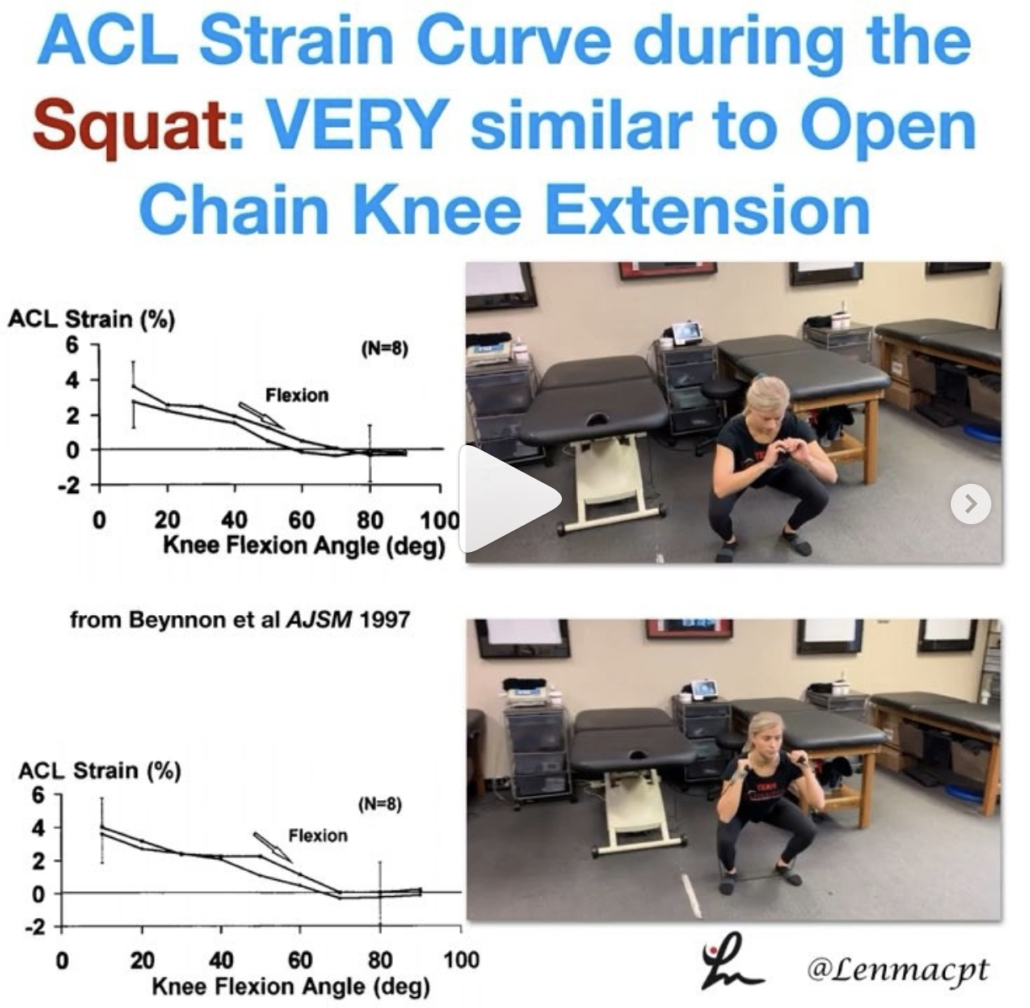
When is it safe to initiate full AROM knee extension after an ACL-PTG autograft?
I posted this video in my the other day and had a ton of people message me about the exercise.
Most people wanted to know how far out of surgery the patient was and when I felt it was safe to begin full, active knee extension after an ACL.
I’ve always been relatively conservative with my rehab (at least I think so) but I wanted to dig a little deeper. I recently saw a post by @mickhughes.physio and he was talking about the Fukuda et al study from 2013.
The study looked at 90-40 knee extensions and ‘ACLR patients can perform 3×10 at a 70% 1RM load through a restricted 45-90deg ROM between weeks 4-12 post-op, and then the same load full ROM from 12 weeks post-op. ‘
It made me dive a bit deeper and I went to my trusty Beynnon et al AJSM studies from the late 90’s. You can see the strain on the ACL decreases as we approach 40 degrees and stays low out to 90 degrees…but is 3-4% strain on the ligament significant?
If you look at the study (yes, it’s only on 8 subjects) you’ll see a similar strain curve for closed chain exercises as well…but we do mini squats immediately after surgery without 2nd guessing!
In 2011, Beynnon et al AJSM showed that an accelerated program that initiated full resisted knee extension (90-0) at 4 weeks showed similar knee laxity throughout the study. The other group initiated full resisted knee extension at 12 weeks. Also, those who underwent accelerated rehabilitation experienced a significant improvement in thigh muscle strength at the 3-month follow-up.
So, what do we do with this data? I have begun to do full, resisted knee extensions with my patients between 4-6 weeks post-op, as long as it’s a patella tendon autograft. For allografts or HS autografts, I tend to delay it a bit longer because of the soft tissue healing that is delayed.
What do you think? When do you initiate full AROM after an ACL? Do you know of a study that definitively says the strain on the ACL graft is detrimental to the healing ligament?

How much Resistance Should we Recommend Open Chain Exercises After an ACL
This is the post from @mickhughes.physio that made me dive a bit deeper into the research on when it MAY be safe to initiate full knee extension from 90-0 after an ACL reconstruction. Check out his post below! ⠀
____________________
So if we can safely perform OKC exercises (knee extensions) as part of ACLR rehab; how heavy can lift?⠀
*⠀
*
This is a question I often get asked. Based on the work by Fukuda et al (2013), ACLR patients can perform 3×10 at a 70% 1RM load through a restricted 45-90deg ROM between weeks 4-12 post-op, and then the same load full ROM from 12 weeks post-op. *⠀
*⠀
From then you can progressively load as per what can be tolerated. Usually the first sign that the knee is unhappy with the load is that the underneath the kneecap will be sore/painful. That’s a sign you need to back the load off a little so the exercise is felt in the quads only. *
If you’re still unsure about OKC exercises (knee extensions) during ACLR rehab read my blog by clicking on the link in my bio ⠀
#ACL #Physio #Knee #Rehab