The Week in Research Review, etc 7-22-18
The Week in Research Review, etc 7-22-18
I’m trying out this new concept of publishing my social media posts into a nice package for a weekly delivery to my subscribers.
- Knee Case Study
- Contralateral ACL Strengthening
- Shoulder Static Stabilizers
- Weighted Ball Research
- Glute Activation
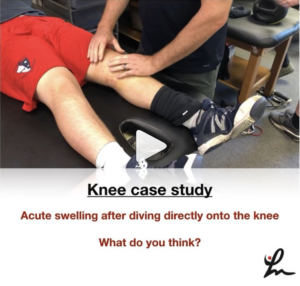
This kid came to me the other day with L knee swelling after sliding headfirst into 2nd base during a baseball game.⠀
Continued to play in the game and even pitched the next day, all without pain or loss of motion.⠀
As you can see from the video, he has a bunch of fluid in his knee, medial ecchymosis (bruising) but full pain-free ROM.
Ligamentous tests appear negative and he has absolutely no pain or stiffness with anything.
I took this video to show what appears to be a bursal sac disruption from the impact of his knee into the ground as he was sliding.
The mechanism fits the presentation and clinical exam.
I advised him to monitor his swelling, wear a knee sleeve and continue his activities per his tolerance.
He is going to touch base with me next week to make sure the fluid is dissipating (and not worsening) and he remains asymptomatic.
What do you think? Am I missing anything? What’s your diagnosis? Tag a friend who may be interested in this case.
Cross-education improves quadriceps strength recovery after ACL reconstruction: a randomized controlled trial. Harput et al Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018
This study looked at a group of ACL reconstructed patients that were divided into 3 groups.
All 3 groups performed the same standardized ACL rehab, but one group was the control group that performed the standardized rehab only.
The other 2 groups did either 3x per week extra concentric knee extensions on their uninjured leg for 2 months (beginning at 1-month post-op through 3-months post-op) or additional eccentric knee extensions on their uninjured leg 3x per week for 2 months between months 1-3 post-op.
💪🏼
They found that the quads strength for the concentric group was 28% greater compared to the control group. 💪🏼
The eccentric group was 31% greater when compared to the control group.
Conclusion: Concentric and eccentric quadriceps strengthening of healthy limbs in early phases of ACL rehabilitation improved post-surgical quadriceps strength recovery of the reconstructed limb.
Pretty crazy stuff and one more reason to work on bilateral strengthening with most of our patients, especially when they’re post-op ACL reconstruction.
Do you work on bilateral strengthening? if not, why? If you do, what other studies have you seen that show similar results?
Tag a friend who may benefit from this study or let’s discuss in the comments section!
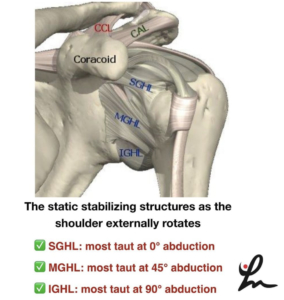
This picture shows a simplified view of the static stabilizers of the shoulder joint. I highly recommend reading a classic paper by Wilk et al 1997 JOSPT that talks about this and cites a paper from Bowen et al Clin Sports Med 1991 @wilk_kevin
When one is picturing these stabilizers, the superior glenohumeral ligament (SGHL) is most taut when the shoulder is externally rotated at 0 degrees of abduction.
As we progress to 45 degrees of GH abduction, we stress the middle glenohumeral ligament (MGHL) as we externally rotate the humerus.
Finally, at 90 degrees of GH abduction, we stress the inferior glenohumeral ligament (IGHL) as we externally rotate. More specifically, the anterior band of the IGHL.
As we internally rotate at 90 degrees of abduction, we stress the posterior band of the IGHL.
These concepts have rehab implications and should be kept in mind when we’re rehabbing people after an injury or surgery.
For example, if someone has an anterior Bankart lesion (front labral repair), then we need to progress them slowly into external rotation, especially at 45 and 90 degrees of abduction.
Another example would be a rotator cuff repair, like the supraspinatus. We would want to progress them slowly at lower degrees of abduction 0-45 degrees but maybe we can progress them a bit quicker at 90 degrees of abduction.
Hope these concepts make sense because they are very important to understand for many patients with shoulder injuries.
Does this make sense? Have you heard this info before? Tag a friend who may benefit from this post!
Effect of a 6-Week Weighted Baseball Throwing Program on Pitch Velocity, Pitching Arm Biomechanics, Passive Range of Motion, and Injury Rates. Reinold et al Sports Health Jul-Aug 2018. @mikereinold⠀
Our 1st of potentially 3 research articles looking at the effects of weighted balls on youth baseball pitchers.
High school baseball pitchers performed a 6-week weighted ball training program.
Players gradually ramped up over the 6 weeks to include kneeling, rocker, and run-and-gun throws with balls ranging from 2oz to 32 oz.
🤔After 6 weeks, the weighted ball group did increase velocity by 3.3%, 8% showed no change, and 12% demonstrated a decrease in pitch velocity. Also of note, 67% of the control group also showed an increase in pitch velocity.⠀
The weighted ball group had a 24% injury rate although half of the injuries occurred during the study, and the other half occurred the next season. There were no injuries observed in the control group during the study period or in the following season.
The weighted ball group showed almost a 5-degree increase in passive shoulder external rotation, also known biomechanically as the late cocking position or layback position.
There were no statistically significant differences between pre- and post-testing valgus stress or angular velocity in either group.
✅Our conclusion: Although weighted-ball training may increase pitch velocity, caution is warranted because of the notable increase in injuries and physical changes observed in this cohort.
Some great Glute 🍑thoughts buy the @theprehabguys. Check out their videos and content for some great ideas that you can add to your practice!⠀
👇🏼⠀
___________________________________________________________________⠀
Episode 705: “Hip Prep for Glute Activation”⠀
.⠀
Tag a friend looking for a glute🍑 killer!⠀
Hip prep is a series of 6 exercises I’ve adopted from my girlfriend @smenzz and her clinic @eliteorthosport. I use it with my patients to prime the glutes and lower body in general before getting into more dynamic and plyometric activities. I will make the statement right now: if done RIGHT, it’s an absolute glute killer & I promise you that you will feel your glutes!⠀
.⠀
I like these 6 exercises in particular for a variety of reasons.⠀
✅They challenge the glutes in all 3 planes of motion.⠀
✅They hit all types of muscle contractions: isometric, concentric, and eccentric⠀
✅They are performed upright in a functional position⠀
✅There is a variety of double leg, single leg, and split stance variations⠀
✅They train proper lower extremity alignment in a variety of hip and trunk flexed/neutral/extended positions⠀
.⠀
The 6 exercises are:⠀
1️⃣3 way clams: 5 per leg per position⠀
2️⃣Side steps: Alternating steps to the left and right starting with 1 step all the way to 5 steps⠀
3️⃣Monster Walks: 10 steps forward, 10 steps backwards⠀
4️⃣W’s: 10 steps to the left, 10 steps to the right⠀
5️⃣Squats: 10 squats⠀
6️⃣Single leg fire hydrants: 30s per side⠀
.⠀
💡Understand that you first need to teach these exercises in isolation first, before throwing someone all 6 at once⠀
.⠀
Have fun!⠀
Hope this helps you keep up to date and fulfill my goal of this website…simplify the literature and bring great content to you so you can apply it 1st thing Monday morning! Happy Reading! 👊🏼
Follow me on Social Media here:












Thanks for all of the great info Lenny! Really appreciate you sharing it with us. Keep it coming Braddah.
thanks a lot, Braddah!