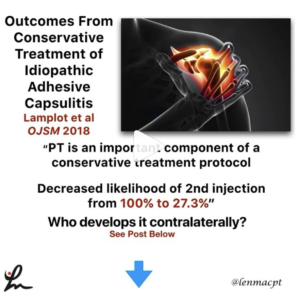
Diagnosed with an elbow UCL Tear- Reconstruction or Internal Brace surgery?
So, you’ve been diagnosed with a UCL tear in your elbow and your world has been turned upside down. Have no fear, many have been there before you and have done pretty well.
But now, there’s a new option for elbow surgery and you’re not sure if it’s right for you. I hope this post can help you decipher the jargon and ease your mind a bit.
Tommy John Surgery
Tommy John surgery has been around since 1974, when legendary Frank Jobe performed the 1st surgery on pro baseball pitcher, Tommy John (shocker!)
It was a pretty epic failure and required a subsequent surgery to fix some of the original issues (massive claw hand due to ulnar nerve issues). Tommy John did return after numerous surgeries to have an amazing MLB career. This set the precedent and baseball has not been the same since.
Fortunately, we have done much better overall. We have improved our surgical techniques and rehab outcomes. Nearly 80%+ of baseball players that have the reconstruction surgery can return to a pretty high level of function. By definition, they will play at the same level or higher compared to their pre-surgery level.
If you don’t believe me, then I suggest you read this article right here. I can attest that the TJ patients that I have rehabbed over the years have done very well. The road is long but most can get back to nearly 100% at around 9-12 months.
Tommy John Surgery Video
Curious to know what the reconstruction surgery looks like? My colleague Dr. Chris Ahmad (who we work with a bunch) presented on his surgery technique recently. Watch this video (as long as you’re not squeamish!) and enjoy!
I usually tell my patients to fast forward 12 months and we can count backwards to figure out the path that we’re going to take.
But that’s not why you are here, right?
You want to know about the internal brace surgery that has taken the TJ world by storm!
Elbow Internal Brace Surgery
This is a relatively new procedure that has been around since about 2013. My friend and colleague Dr Jeff Dugas began doing this procedure in Birmingham, AL when I was down there. I got to see the early results 1st hand and was excited but skeptical.
Baseball players were returning to their sport in 6-8 months versus the 1 year that we had seen in a full TJ surgery.
Why a quick return after surgery?
Why have them return sooner if the surgeon is not using the patient’s native tissue?
Who should get this surgery anyway?
We didn’t necessarily know, but like any other orthopaedic surgery, we had to wing it a bit. We had to figure out a protocol that was appropriate for the tissues involved.
I was there in Birmingham with another friend and colleague, physical therpaist Kevin Wilk. I helped put together the early protocols and was excited by the potentials.
The thought is that the collagen dipped tape that is re-enforcing the repaired ligament is stornger than the native ligament. Its fixation to the bone is strong. A quicker return to throwing and sport is possible, because of those reasons.
Its worked for the ankle and so why can’t it work for the elbow too?
Internal Brace Surgery Specifics
This internal brace surgery was developed by surgical company Arthrex. It’s pretty neat to see how it has taken on a whole world of uses, including in the knee and ankle. Its many uses has helped numerous athletes return back from their injuries quicker than ever.
See Tua at the University of Alabama, for examaple. He had a high ankle sprain and retuned to the field ~3 weeks after his ankle surgery. Again, surgery performed by my friends Dr Norman Waldrop and Dr Lyle Cain, of Andrews Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic Center. They’re studs and surgeons that i’d highly recommend!
Who benefits the most from Internal Brace surgery?
For this elbow surgery, the internal brace is most appropriate for the athlete that has a UCL sprain that is not complex. Most times, they won’t know until they’re in the surgery if the internal brace is appropriate.
If it is appropriate, then surgical consent probably happened before the surgery. The doctor won’t know if the repair is appropriate until he/she can visualize the tissue directly. A decision is made on the spot even if the MRI said something differently.
Why try the internal brace?
I basically recommend this surgery for my athletes who don’t have a lot of time.
Let’s say they sprain the ligament in the offseason, like in November of their junior year in high school, for example. If a full-blown TJ reconstruction was done, then they’d be out until at least the following November (remember my 12-month comment earlier). That would mean no junior year baseball or Summer ball. That would also mean no exposure for college recruiting!
But wait, there’s an alternative! Internal Brace repair surgery…see the video here!
…or here by Dr Jeff Dugas:
In the internal brace situation, you could have the surgery in November and be back for some of your High School season and most likely for that important Summer travel season.
But remember, the ligament can’t be chewed up a lot. That decision will be made intraoperatively. Be ready to wake up from surgery with news that a full TJ reconstruction had to be done.
But for many, an internal brace repair is possible. And a quicker return may be possible too.
Should you do this surgery?
For those considering it and fit the requirements, then I’d recommend it. Just keep in mind that we really don’t have too many long term outcomes.
But for the High School or College athlete looking to play a few more years, then I’d say go for it.
For the HS or college pitcher who has aspirations of playing pro ball, then I’d recommend the full reconstruction. We just know more about the surgery and long term outcomes. it’s tried and true in every way.
That’s not to say that the internal brace procedure cannot be the gold standard surgery in a few years. That is quite possible. I really hope to update this blog post in the future and say that I was wrong.
But as of now, I would recommend the reconstruction for the pro athlete or amateur athlete looking to play pro ball. Otherwise, the internal brace procedure is a very strong option for many pitchers (or even positional players looking to get back quicker).
Summary- Who should get this surgery?
Pitchers or positional players that don’t have much time before their next season and NEED to play. But the tissue needs to be repairable and not beat up (this is the key!)
Consult your surgeon to discuss this but they won’t know until they’re in your elbow and you’re out cold from anesthesia.
Good luck…it’s a long and winding road but most do well. I’ve treated a lot of these cases and no 2 are ever the same. There’s always a glitch and a freak out period but it often works out in the end!