The Week in Research Review, etc 8-5-18
The Week in Research Review, etc 8-5-18 we discuss a wide variety of topics including:
- Long-term disability if weak during adolescence
- Using heat during rehabilitation
- OKC vs CKC exercises after an ACL
- Live look at an Achilles rupture (with sound too!)
- A fun look at the different types of PT’s
- Congrats to all of the newly licensed PT’s!
Muscular weakness in adolescence is associated with disability 30 years later: a population-based cohort study of 1.2 million Swedish men. Henriksson et al BJSM June 2018.
Conclusion: There was a strong association between muscular weakness and disability. A combination of muscular weakness and low aerobic fitness was an especially important risk factor for disability. This adds weight to call for muscular strength and fitness-enhancing exercise for adolescents in all BMI categories.
This study out of Sweden looked at the associations of muscular strength in adolescence with later disability pension.
A total of 1 212 503 adolescent males aged 16–19 years, recruited from the Swedish military conscription register between 1969 and 1994.
Moral of the story: exercise as an adolescent may help to reduce issues later in life, including the potential for disability.
Taking it 1 step further… why is physical education being cut out of school requirements when studies like this show the potential negative effects of inactivity?!
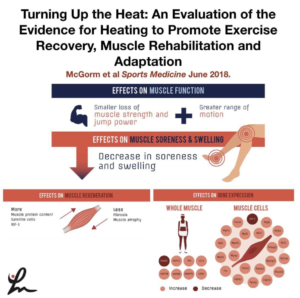
Turning Up the Heat: An Evaluation of the Evidence for Heating to Promote Exercise Recovery, Muscle Rehabilitation, and Adaptation McGorm et al Sports Medicine June 2018.
Key Points: Animal and human trials have shown that various forms of heating can be used in conjunction with exercise or stress to enhance recovery, adaptation and limit muscle atrophy.
Heating muscle activates protective mechanisms, reduces oxidative stress and inflammation, and stimulates genes and proteins involved in muscle hypertrophy.
Further studies highlighting the differences between various heating modalities will help inform athletes and coaches on the best heating practices for specific situations.
This article has a ton of great information that I highly recommend any PT, strength coach, athletic trainer or massage therapist.
It is a review of the literature and there are still many questions to be answered so, as always, take with a grain of salt.
I am a fan of heating before treatment…I do it daily with 99% of the clients that I see and they love it…so that says something.
What do you think? Do you like to heat your clients up before treatment or before a workout? Tag a friend that may benefit from this post! Thanks, guys!
The Effect of Open- Versus Closed-Kinetic-Chain Exercises on Anterior Tibial Laxity, Strength, and Function Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Perriman et al JOSPT July 2018 Level 1a
FINDINGS: There was no significant difference in anterior tibial laxity, strength, patient-reported function, or physical function with the early or late introduction of open-kinetic-chain exercises in those who have had anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction, when compared to closed-kinetic-chain exercises, at all follow-up time points.
They wanted to determine whether OKC quadriceps exercises result in differences in anterior laxity, when compared to CKC exercises, at any time point following ACLr.
Also, they wanted to determine whether there are differences in strength, function, quality of life, and adverse events with OKC quadriceps exercises when compared to CKC exercises at any time point.
Overall, calculated effect sizes showed a slight increased laxity in the OKC groups, particularly for the hamstrings graft. The⠀
pooled difference was not statistically significant (P>.05)
When considering all graft types, there was low- to moderate-quality evidence from 3 studies suggesting that there were no between-group differences in laxity at any time point when OKC exercises were introduced earlier than 6 weeks post ACLR, compared to CKC exercises.
There seemed to be a trend that showed early OKC knee extension was safer after a PTG than a hamstring autograft but protocols varied so data was inconsistent.
Of interest to me, they said “The early introduction of OKC quadriceps exercises did not appear to offer additional significant benefits in function and strength for the average patient post ACLR; therefore, this early introduction is questionable, especially in patients with a hamstring graft.
From Twitter’s @IrineuLoturco showing the moment this athlete ruptured their achilles tendon. Pretty impressive and you can see the eccentric loading of the tendon that caused the rupture. See his original post below…
A very impressive recording of the exact moment when an elite sprinter had an acute and complete rupture of the Achilles tendon. Pay attention to the “boom”.
[REPOST] If there was an ESPY for a post by a PT then @theperformancedoc would definitely get it for these videos! Great job and keep pumping out great content. Give him a follow if you haven’t already!
👇🏻
💥Different Types of Physical Therapists In the Real World💥 SWIPE 👉🏽 (Turn on 🔊) Sometimes we have trouble “turning it off” when we are outside of the clinic. Which one are you?! Tag, Comment, & Share with a Physical Therapist‼️
–
▪️
#ThePerformanceDoc #RehabWithTheDoc
#TeamMovement
Congrats to all of the newly licensed PT’s out there…Welcome to the profession!
My advice to you:
Stay humble and put the patient first, always
Keep learning and try to avoid complacency
The road will seem rough but it does get a little easier. Get experience…as much as you can. Each interaction with a patient is a snapshot to help guide your future interactions.
Put yourself in their shoes… give them the best experience as you would expect to receive if you were sitting on the plinth being asked questions.
Follow people on social media that help you to learn and keep an open mind. Don’t get pulled into 1 system. Take a little from each and package it nicely.
The research is often biased. Opinions come and go. Stay somewhere in the middle…remember the bell curve, always!
Each “system” has huge overlap despite their ‘trademarked’ proprietary information…they all involve motion and strengthening. That’s the key to PT- keep people moving and keep them stronger…or at least keep them positive and hopeful.
I recently wrote a blog post discussing the evolution of a PT. Take a look…the link is in my bio on Instagram.
These words are the basis of my practice. Take what you think is important and apply it to your practice. Good luck, now work on your dives!
A great week of content that I hope you found valuable and willing to share with your friends and colleagues! Thanks for reading!