The Week in Research Review, etc 11-19-18
Great ‘Week in Research Review, etc 11-19-18’ that I hope you find helpful to your practice.
I’ve always touted the importance of the subjective portion of the exam so I wanted to share a slide from a recent talk I gave to a group in Canandaigua, NY. Obviously, the squat is a fundamental movement and I wanted to give some basic positions that I use to help assess. So excited that I’ve launched a brand new Medbridge course that helps the rehab specialist better eval and treat the baseball pitcher. On my YouTube channel, I discussed my thoughts on setting the scapula with various upper and lower body exercises. And finally, my co-worker Kiefer Lammi discusses the landmine with exercise.
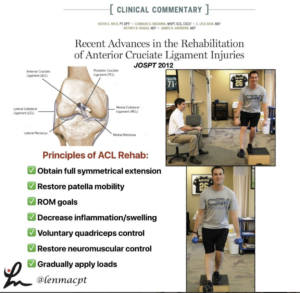
Importance of the Subjective Exam
Assessing the Squat
My New Baseball Medbridge Course
Set the Scapula with Shoulder Exercises?
6 Ways to use the Landmine by @kieferlammi
💥Subjective the most important aspect of the Evaluation💥
This slide, taken from this past weekend’s course in Canandaigua, NY is always a favorite of mine.
I try to keep a slide like this in all of my lectures because I have found that this portion of the examination can give the rehab specialist a huge look into what is going on with the person in front of them.
Don’t get me wrong, I still consider the biomechanical aspect of what may be causing their symptoms.
It often comes down to a tissue capacity issue but it’s up to me to determine the appropriate course of treatment.
These questions will help build confidence in your client and guide the early stages of rehab.
Do you have any specific questions that you like to ask your clients during their 1st few sessions? Remember, these questions are just not for the evaluation. You should be asking these questions periodically to gauge progress and help guide the next phases of rehab, too!
🔅Assessing the Squat 🔅
Squatting is a fundamental movement that all of us have to do on a daily basis.
Utilizing several different positions can help the rehab specialist better assess the squat and develop a treatment plan that enables their client the ability to improve their squat pattern.
In the above videos, I have utilized 3 different squat patterns and will outline them by the degree of difficulty.
✅The Overhead Squat- by far the most challenging version which challenges the shoulders, thoracic spine, lumbar spine, pelvis, knee and ankles.
A movement limitation at any of these joints will most likely cause the squat pattern to break down. Using overhead resistance would further challenge the system and potentially cause the squat to further breakdown.
✅Arms Crossed Chest Squat- alters the challenge by taking most of the shoulder and thoracic spine out of the equation and isolates the motions to the lumbar spine, hips, knees and ankles.
I often use this position as my fundamental motion because most people don’t have to squat with any weights over their head. This position, in my opinion, should be the most informational and utilized.
✅Counter-weight Squat
This position changes the center of mass by moving some of the weight distribution more anteriorly (front) and making the squat motion slightly easier. I use this position as a regression, for some, which allows them to squat with less stress and potential difficulty.
There are many other variations to the squat that you can make but I wanted to highlight a few of the major changes that you cause successfully. Assessing the squat is essential and can give the rehab specialist a nice picture of the function of multiple joints during a common movement.
My BRAND NEW course on Medbridge’s platform
…that helps the sports and ortho rehab specialist (PT, OT, ATC) better understand the anatomy and biomechanics involved in the baseball pitching motion.
Advanced Rehab for the Baseball Pitcher to Improve ROM & Strength@medbridge_education
The goal of this course was to allow the clinician to be able to evaluate and treat the baseball pitcher using evidence-based guidelines that I use on a daily basis.
Numerous research studies discuss the adaptive changes that occur with the pitching motion followed by numerous videos to help guide the treatment process.
If you’re already a Medbridge subscriber, then you have immediate access today.
If you’re not a Medbridge member, then you can use my promo code “Lenny2018” to save up to 40% off a yearly membership.
This gets you unlimited CEU’s for 1 year and potential access to their online HEP and a lot more!
Students can also get 1 year of unlimited courses (no CEU’s) by using promo code LennySTUDENT2018 and pay only $100.
Check out my other shoulder courses as well by using the Medbridge platform…along with many other great speakers!
Hope you enjoy and good luck!
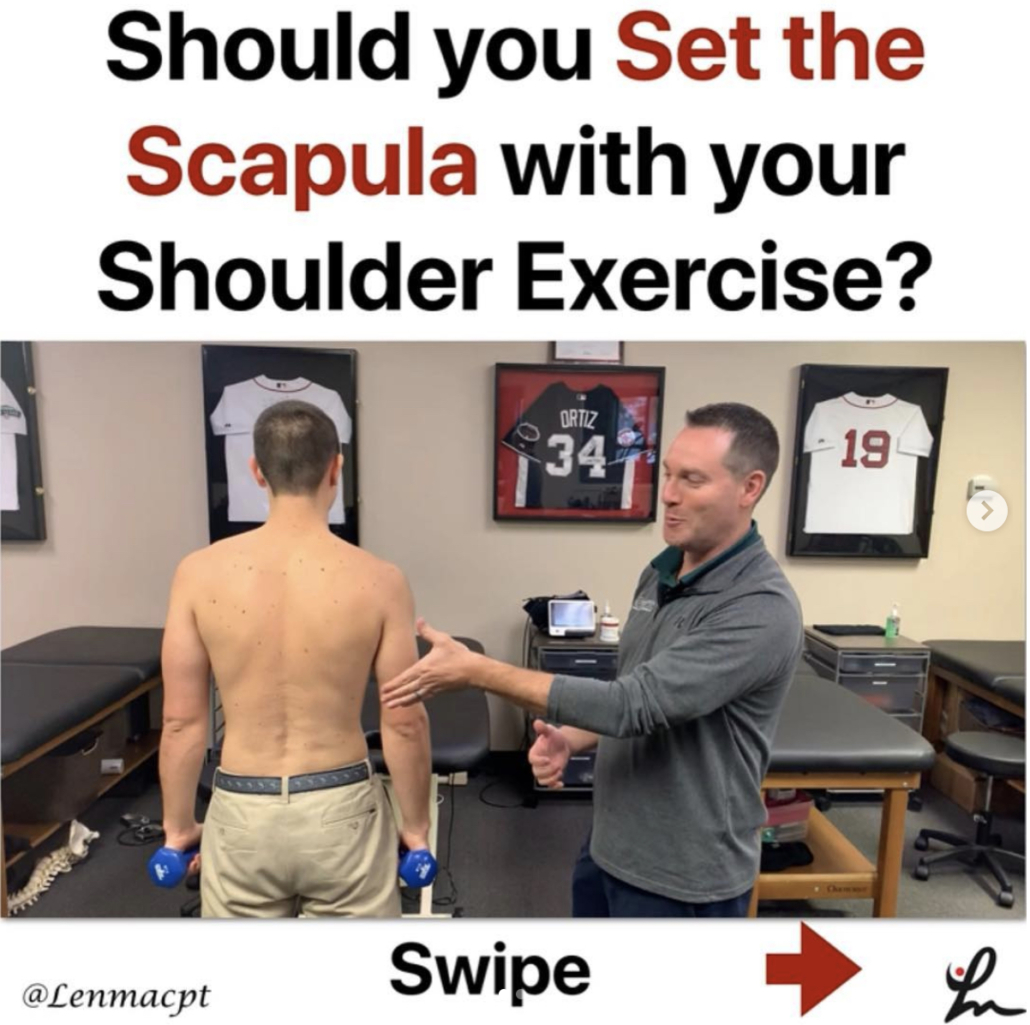
💥Should you Set the Scapula with your Shoulder Exercise?💥
In this video excerpt from my YouTube channel, I wanted to discuss my opinion on setting the scapula during common exercises.
I think there’s an obvious role for setting the scapula during a heavier lower body lift like a deadlift.
But for a classic upper body exercise like the Full Can (Scaption Raises) or prone T (horizontal abduction), prone Y (Prone full can), etc then I definitely want the scapula to freely move along the rib cage.
I did a quick literature search and didn’t see anything obvious that helped to guide my thoughts so most of this is anecdotal. Check out the video and comment below.
Do you coach your clients to set their scapulae before a rotator cuff workout? If so, why? If not, do you think we should reconsider?
6 WAYS TO USE THE LANDMINE!
Great post from our own @kieferlammi at @championptp on various ways to use the landmine in your client’s workout routine.
If you don’t have one, then I’d highly recommend you try to obtain one because they are highly versatile and can be used in many stages of rehab. See Kiefer’s original post below 👏🏼
_____________
6 WAYS TO USE THE LANDMINE!
The landmine attachment is a super versatile tool for loading that is traditionally known for being used for angled pressing variations. While that’s probably my most programmed use for it, it also provides benefit to a ton of other movements by placing the load and direction of force at a bit of an angle, which can help to promote a particular path of movement, like sitting back more in a squat or lunge. Here are 6 of my favorite ways to use the landmine:
1️⃣1-Leg RDL
2️⃣Split Stance Row
3️⃣Reverse Lunge
4️⃣Deadlift
5️⃣Squat
6️⃣Russian Twist⠀
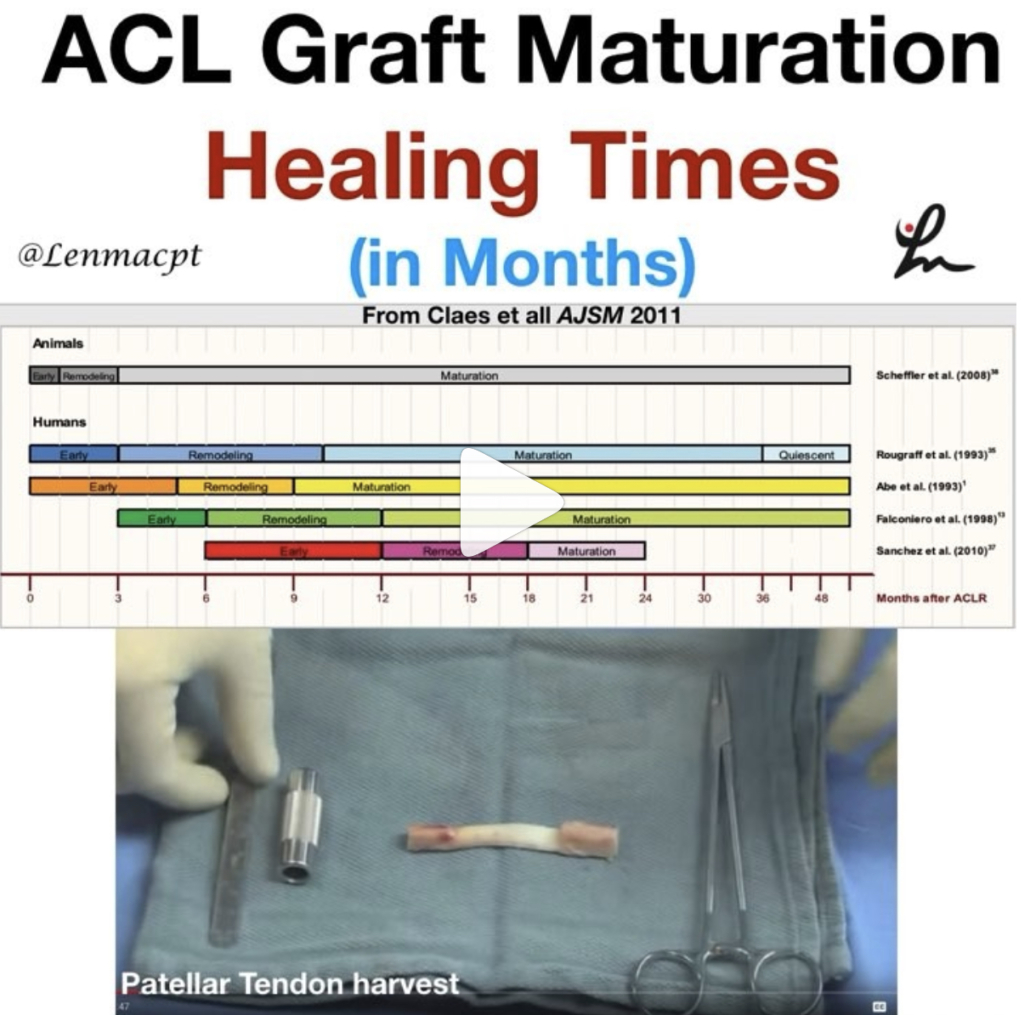
Save 25% off our OnLine Knee Seminar Course…all this week!
Expires Sunday, November 25th at midnight ET

If you want to learn more about how I treat ACL’s or the knee in general, then you can check out our all online knee seminar at www.onlinekneeseminar.com and let me know what you think.
We cover the anatomy, rehab prescription, ACL, meniscal injuries knee replacements and patellofemoral issues. Furthermore, the course covers both the non-operative and post-operative treatment.t
This is an awesome course if you’re interested in learning more about rehabilitating the knee joint. And if you’re a PT, there’s a good chance you can get CEU’s as well.