The Week in Research Review, etc 9-10-18
Lots of good stuff this past week. We talked:
- Dr. Andrews knowledge bombs
- Frozen Shoulder video
- AC joint Classification
- Whether we should return our ACL patients at 6 months post-op
- Eric Cressey quote on failing rehab
What I have learned about being successful as an orthopedic surgeon by Dr James Andrews
Great read by my friend, mentor and colleague who I was fortunate to work with from 2002-2014, before moving back home to Boston to help open @ChampionPTP with @mikereinold.
I learned so much from my interactions with him and how he handled each and every case. His approach has been the standard by which I carry myself as a PT
In this paper, he talks about: ⠀
✔️Availability⠀
✔️Communication⠀
✔️Compassion⠀
✔️Gentleness⠀
✔️A true love of caring for my patients
He also talked about being successful with a ‘purpose driven life’ and discusses 16 key recommendations to a successful orthopaedic career.
Take a look at this article and implement as much as you can tomorrow and every day thereafter.
Happy reading…share with a friend or colleague in the comments section below!⠀
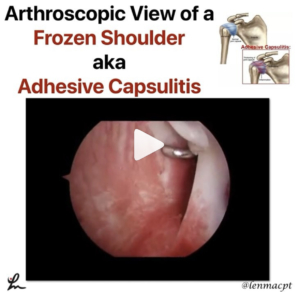
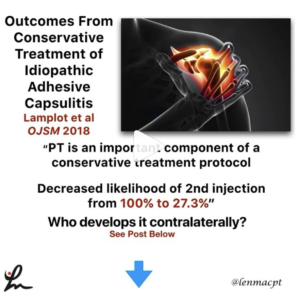
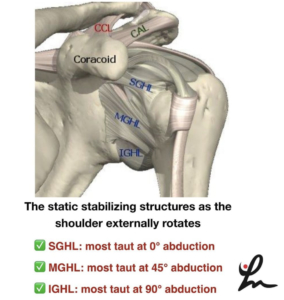
Frozen Shoulder or adhesive capsulitis can be debilitating and frustrating for the patient.
This video shows why! Look at all of that red and inflamed tissue of the shoulder capsule. Those neovascular changes are a classic sign of frozen shoulder and the main reason why anti-inflammatories are probably effective in the early stages of the disease.
The pain associated with this presentation is often the main limiting factor, combined with the eventual capsular scarring/contracture that develops soon after.
This scarring leads to a loss of joint arthrokinematics, which leads to loss of mobility, functional loss and atrophy. This spiral effect can last months if not years for some.
Regaining mobility, strength and normal function is not guaranteed but PT can help speed up the process a bit by educating, guiding and mobilizing the patient.
if I see someone in an early stage of frozen shoulder, I usually recommend a cortisone shot followed by more PT to help maintain the patient’s shoulder ROM/strength.
What do you recommend? Any tests you use to help diagnose adhesive capsulitis?
Tag a colleague who may benefit from this post…thanks!⠀
With football season here, we’re going to hear a lot of talk about #shouldersaparation or AC joint sprains
The different Grades (Rockwood Classification) of AC Joint sprains are:⠀
1️⃣ AC ligament sprain, AC joint intact, CC ligaments intact⠀
2️⃣AC Joint disruption, Slight vertical separation of ACJ, CC ligament sprain, CC distance wide⠀
3️⃣AC ligament disruption, AC joint dislocated, CC ligaments torn⠀
4️⃣AC ligament disruption, AC joint dislocated, Clavicle displaced posteriorly into Trapezius, CC ligaments completely torn⠀
5️⃣AC ligament disruption, AC joint dislocated, CC ligaments completely torn,⠀
CC distance 100 to 300 % > than normal side.⠀
6️⃣AC ligament disruption, AC joint dislocated, CC ligaments completely torn, Clavicle in subcoracoid position.
I saw this video that @drroddymcgee put out on #Twitter and loved the visual effects to help simplify the typical tissues involved with each type of AC Joint sprain. You can slo find them at @thesportsdocs00 on Twitter too.
Hope it helps to put the AC joint sprains in a better view for you. Share with a colleague who may have an interest…thanks!
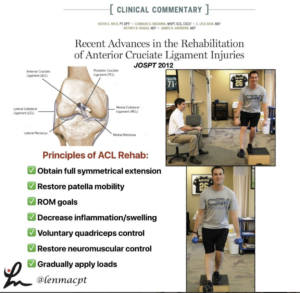
Return to play after an ACL is a complex decision that involves many variables. The research is telling us a 6-month return to play is too quick and should be delayed up to 9 months.
During that time, the focus of the rehab needs to be on gaining strength, power, and confidence in the patient’s lower body, particularly the quadriceps.
✅ 51% reduction for each month return to sport was delayed until 9 months after surgery…research by Grindem et al BJSM 2016.
Hewett et al have advocated for a possible 2-year return to play wait time to account for graft healing and time for the full strength, power and confidence to return.
I have adjusted my practice to educate my clients for a 9-month return and map out a timeframe from the beginning so they buy into that thinking. Often times, doctors will place a 6 month time for RTP and I have to overcome that thinking and ‘convince’ my clients that it’s too soon.
I think that much time is needed to get the quadriceps muscle back completely and to gain the full confidence in the limb through dynamic activities.
Do you agree? What do you recommend and do you agree with Coach Saban’s answer on RTP at 6 months? 😜
Tag a friend who would benefit from seeing this post or at least seeing Coach Saban…thanks! #RTR #notreally #neutral#switzerland
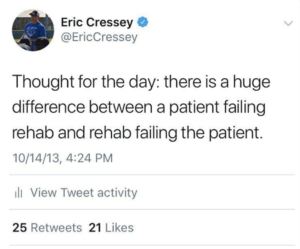
Failing Rehab
As a PT, this really hit home with me and thought @ericcressey nailed it! See his original post below. @cresseysportsperformance 👇🏻
As with any professional offering – training, accounting, contracting, landscaping, or a host of other services – you’ll see good and bad rehabilitation scenarios. Make sure you do your homework about not only a rehab specialist’s experience and credentials, but also the business model in which he/she operates. 😵#cspfamily #sportsmedicine#rehab #physicaltherapy #physicaltherapist#athletictrainer #athletictraining#sportsperformance #rehabilitation