Tag: knee surgery
-
Simplifying ACL Rehab
—
by
ACL surgery continues to be a huge focus in the literature and in our outpatient rehabilitation settings. Numerous studies focus on return to play guidelines and retear rates. Social media is all over the place, most times. Let’s try to make things simple and set the stage early. Paralysis by Analysis- What ACL tests are…
-

ACL Volume Changes over a Women’s Soccer Season
I’m a bit interested, confused and looking to seek more on this open access paper that just came out in March of 2019 looking at the effects of season-long participation on ACL volume in female intercollegiate soccer athletes. The title of the paper is: “Effects of season-long participation on ACL volume in female intercollegiate soccer…
-

The Week in Research Review, etc 12-17-18
—
by
Not a lot this week…sorry folks. Focusing a bit more on other projects. The Week in Research Review, etc 12-10-18 included only 3 posts but they definitely made some waves. Especially my latest Instagram post on burn-out in the PT field. Check it out and chime in…it’s never too late to like a post and comment…
-

The Week in Research Review, etc 12-10-18
—
by
This week we’re still playing with formats and learning these Instagram changes. With that, in the week in research review 12-10-18, we discussed many topics that I wanted to share! Surgery vs Physical Therapy for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome View this post on Instagram A post shared by Lenny Macrina MSPT, SCS, CSCS (@lenmacpt) on Dec…
-
Knee Bracing Immediately After an ACL Reconstruction
I recently came across a Facebook post that discussed bracing immediately after an ACL reconstruction and I was intrigued. I read some of the comments and chimed in with my observations and opinions. In turn, a multi-platform discussion revealed many new details. I wanted to briefly share some of the research and the discussions that…
-

The Week in Research Review, etc 10-15-18
—
by
in ACL, baseball, DPTstudent, elbow, exercise, hip, knee, Physical Therapy, rehabilitation, Research, rotator cuff, ShoulderThis week I posted a lot of research and thoughts on shoulder and knee rehab, particularly after an ACL injury. I also shared some others posts that really complimented my posts so there’s some bonus reading to do too. Hope The Physical Therapy Week in Research Review helps your Monday patients and beyond! Take a read and…
-
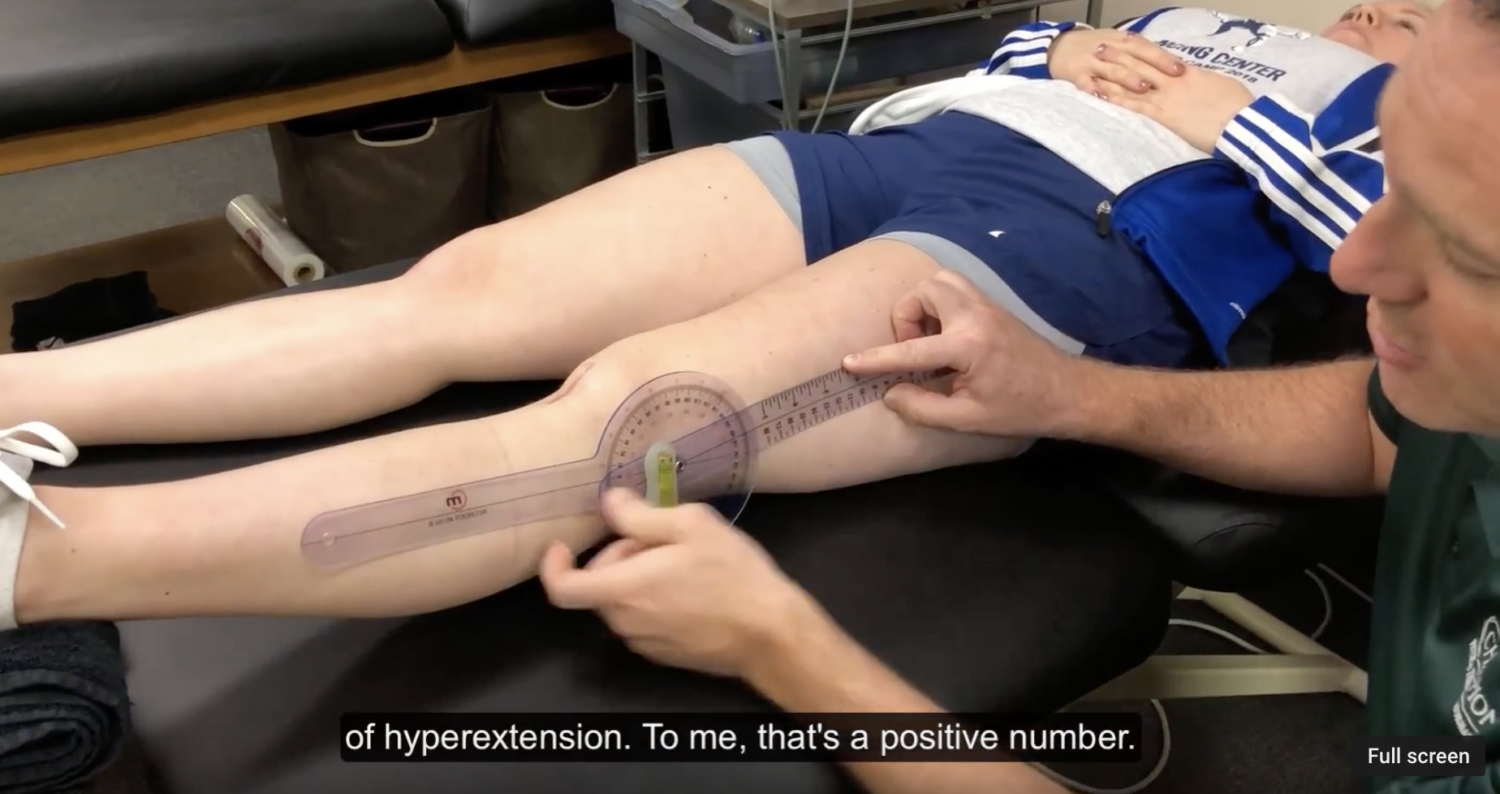
Documenting Knee Extension Range of Motion
I’ve talked a lot about the importance of regaining knee extension range of motion (ROM) after a knee injury or surgery. In this post, I want to talk about how exactly I believe we should be documenting knee extension range of motion. I think it’s important because I hear many other medical professionals and students document differently.…