Tag: meniscus
-
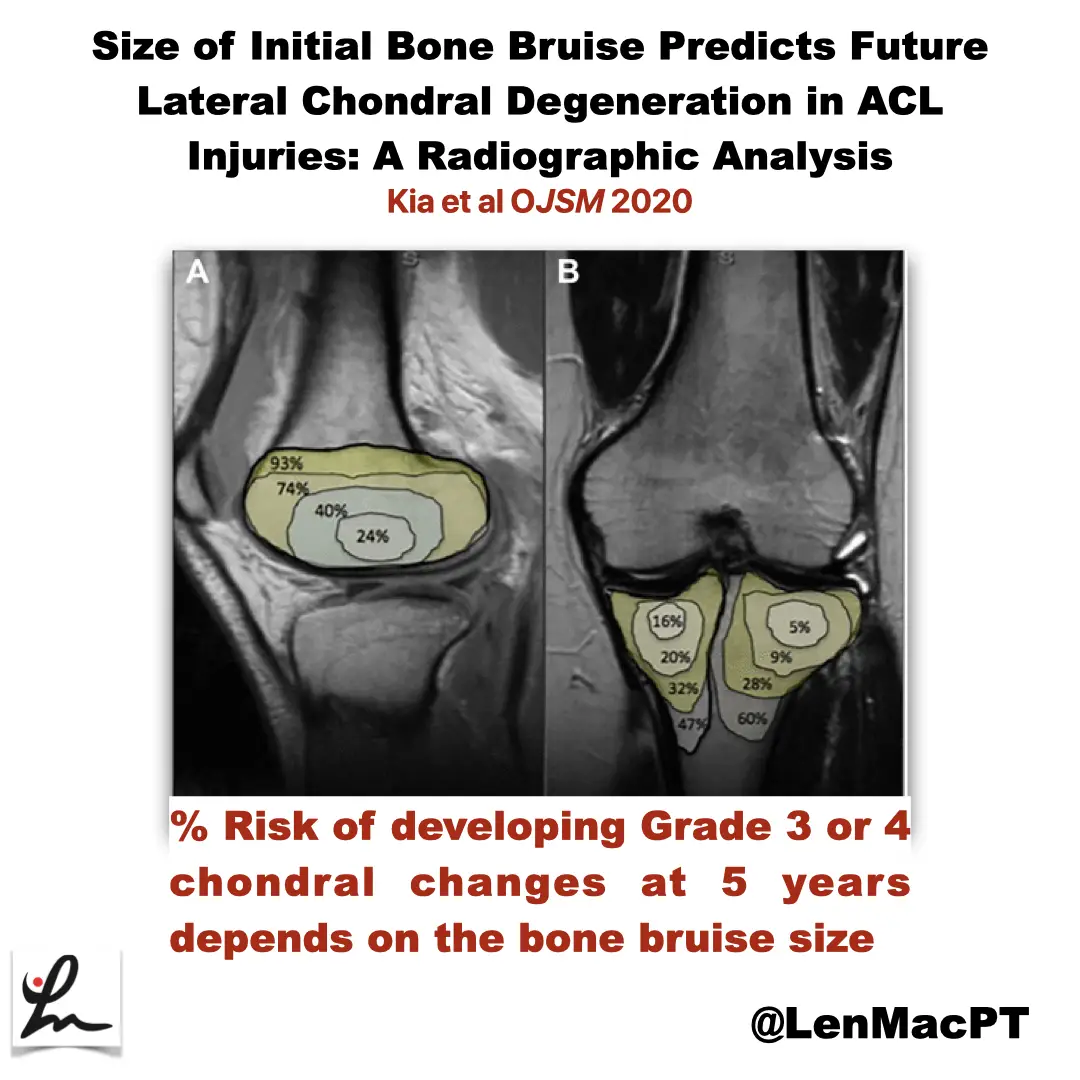
ACL tears and bone bruises
—
by
Research Review Not sure if you saw my recent post on social media about bone bruises after an ACL tear so I wanted to discuss it further here. In this study, the authors looked at the incidence of radiographic chondral changes (without correlation with clinical and functional outcomes) on MRI 5 years after the ACL…
-

The Week in Research Review, etc 12-10-18
—
by
This week we’re still playing with formats and learning these Instagram changes. With that, in the week in research review 12-10-18, we discussed many topics that I wanted to share! Surgery vs Physical Therapy for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome View this post on Instagram A post shared by Lenny Macrina MSPT, SCS, CSCS (@lenmacpt) on Dec…
-
Diagnosing meniscus tears: What’s the literature telling us now?
Meniscal tears are commonly observed in an outpatient physical therapy setting. The ability of a PT to evaluate a patient’s knee and diagnose a meniscus tear can help guide the treatment plan for that patient. Having specific tests that can accurately and quickly pick up a meniscal tear are valuable. Lots of test options but stick…